ACTIVE TRANSPORT
advertisement

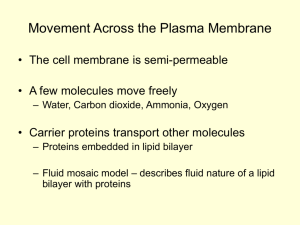
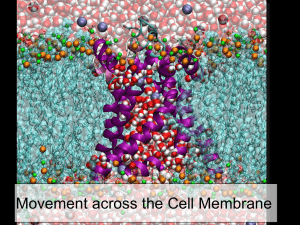
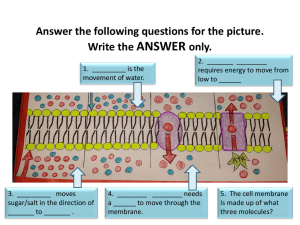
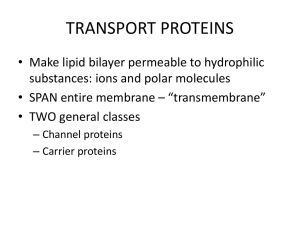
Warm up Type of Transport Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion What moves? Solute or Solvent It moves towards an area of higher or lower concentration? Moves Down or up the concentration gradient? Does it require Energy? Warm up Type of Transport What moves? Solute or Solvent Diffusion Moves Down or up the concentration gradient? Solute To Lower Concentration Down the Concentration Gradient Solvent To Higher Concentration Up the Concentration Gradient Solute To Lower Concentration Down the Concentration Gradient Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion It moves towards an area of higher or lower concentration? Does it require Energy? NO ENERGY Required NO ENERGY Required NO ENERGY Required ACTIVE TRANSPORT Chapter 5 pg. 103-106 Active Transport • Requires energy! • Molecules move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration • Move against the concentration gradient 1. Membrane pumps 1. Membrane pumps • Pumps – Transport proteins that use energy – (low high) • Protein transfers the molecule to the other side. • Sodium-Potassium Pump: transports Na+ and K+ against (not down) gradient 2. Endocytosis • Bring large molecules into cell 1. Material is engulfed by cell membrane. 2. Membrane makes a pouch. 3. Pouch then pinches off and makes a vesicle. 4. Vesicle binds with lysosome. 2. Endocytosis • Phagocytosis: A form of endocytosis in which immune cells attack and kill bacteria 3. Exocytosis • Moving large particles out of the cell (the reverse of endocytosis) Draw This 1. Finish Grape Lab 2. Finish “Transport Review” DUE MONDAY • Grape Lab • Transport Review • Cell Chosen Chart (on model directions)