DIFFUSION & OSMOSIS
advertisement

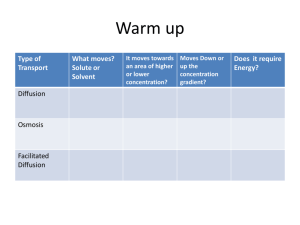
CELL MEMBRANES & DIFFUSION MIXTURE • TWO OR MORE ELEMENTS THAT ARE PHYSICALLY MIXED TOGETHER SUSPENSION • FLUID AND NONDISSOLVED MATERIAL SOLUTION • ALL COMPONENTS ARE EVENLY DISTRIBUTED AND DISSOLVED SOLUTE • SUBSTANCE BEING DISSOLVED SOLVENT • Substance that dissolves the solute SOLUTE • SUBSTANCE BEING DISSOLVED SOLVENT • Substance that dissolves the solute CONCENTRATION • AMOUNT OF SOLUTE PER SOLVENT • Mass / Volume EVERYTHING MOVES FROM HIGH TO LOW DIFFUSION • MOVEMENT FROM HIGH TO LOW CONCENTRATION • Concentration Gradient: the differences in concentration of two mediums ↑ Concentration Gradient = ↑ Diffusion Osmosis: the diffusion of water EQUILIBRIUM • CONCENTRATION OF SOLUTE IS THE SAME THROUGHOUT THE SYSTEM TONICITY DIFFERENCE IN WATER CONCENTRATION OF TWO SOLUTIONS SEPARATED BY A PERMEABLE MEMBRANE HYPERTONIC MORE SOLUTES IN THE AREA HYPOTONIC LESS SOLUTES IN THE AREA ISOTONIC EQUALS AMOUNTS HYPERTONIC 10% STARCH = WATER DIFFUSES OUT OF CELL, CELL SHRINKS 30% STARCH HYPOTONIC 30% STARCH = WATER DIFFUSES INTO CELL, CELL EXPANDS 10% STARCH ISOTONIC 20% STARCH = NO NET MOVEMENT 20% STARCH Nucleolus Nucleus Rough E.R. Cytoskeleton Lysosome Smooth E.R. Mitochondria Ribosomes Vacuole Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus The Plasma Membrane of cells are made up of a PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER Hydrophilic Head “water-loving” Hydrophobic Tails “water-fearing” The Plasma Membrane of cells also have PROTEINS and CHOLESTEROL • • Help movement across the membrane; protein channels Detect materials outside the cell • Help keep the membrane fluid and wavy ___IN___ Nutrients - sugars (glucose) - proteins - fats Salts O2 H2 O ___OUT___ Waste - ammonia - salts - CO2 Products - Proteins H2O • INSIDE • Uncharged smaller particles can pass through the membrane Charged particles (+/-) or large particles cannot SALT +/- OUTSIDE LIPIDS CO2 WASTES O2 STARCH Large and/or charged particles must use Transport Proteins or Protein Channels to pass through the plasma membrane Simple Diffusion vs. Facilitated Diffusion • Move from HIGH to LOW directly • Move from HIGH to LOW through the lipid bilayer through a transport protein Passive Transport: diffusion occurs down the Concentration Gradient Sometimes, transport needs to occur AGAINST the Concentration Gradient Example: Glucose Cells must use ACTIVE TRANSPORT to go against the gradient Active Transport uses ATP Energy to push materials from LOW to HIGH concentration Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Passive Transport Simple Diffusion shipping out of the cell shipping into the cell https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=prfMUwjobo8 How does endocytosis and exocytosis work? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XdCrZm_JAp0