You Light Up My Life
advertisement

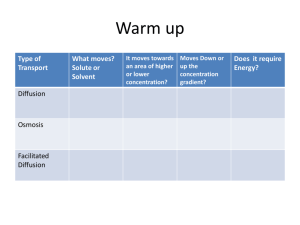
A Closer Look at Membranes Chapter 5 5.1 Lipid Bilayer • Main component of cell membranes • Gives membrane its fluid properties • Fatty acid tails sandwiched between hydrophilic heads lipid bilayer fluid fluid Figure 5.2c Page 82 Fluid Mosaic Model • Membrane is a mosaic of – Phospholipids – Glycolipids – Sterols – Proteins • Most phospholipids and some proteins can drift through membrane 5.2 Membrane Proteins adhesion protein receptor protein communication protein recognition protein passive transporter active transporters Figure 5.5 Page 85 5.4 Selective Permeability O2, CO2, glucose and other large, polar, and other small, nonpolar water-soluable molecules; ions, molecules; some water water molecules molecules Membrane Crossing Mechanisms Diffusion across lipid bilayer Passive transport Active transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Concentration Gradient • Means the number of molecules or ions in one region is different than the number in another region • In the absence of other forces, a substance moves from a region where it is more concentrated to one where it’s less concentrated - “down” gradient Diffusion • The net movement of like molecules or ions down a concentration gradient • Although molecules collide randomly, the net movement is away from the place with the most collisions (down gradient) Factors Affecting Diffusion Rate • Steepness of concentration gradient – Steeper gradient, faster diffusion • Molecular size – Smaller molecules, faster diffusion • Temperature – Higher temperature, faster diffusion • Electrical or pressure gradients Example of Diffusion 5.6 Transport Proteins • Span the lipid bilayer • Interior is able to open to both sides • Change shape when they interact with solute • Move water-soluble substances across a membrane Passive and Active Transport Passive Transport Active Transport • Doesn’t require energy inputs • Solutes diffuse through a channel inside the protein’s interior • Net movement is down concentration gradient • Requires ATP • Protein is an ATPase pump • Pumps solute against its concentration gradient Passive Transport glucose transporter solute (glucose) high low Stepped Art Figure 5.10 Page 88 higher calcium concentration Active Transport lower calcium concentration ATP Pi ADP Stepped Art Figure 5.11 Page 89 5.7 Osmosis • Water molecules tend to diffuse down water concentration gradient • Total number of molecules or ions dictates concentration of water • Tonicity - relative solute concentrations Tonicity 2% sucrose solution distilled water 10% sucrose solution 2% sucrose solution Hypotonic Conditions Hypertonic Conditions Isotonic Conditions Figure 5.13 Page 90 Fluid Pressure • Hydrostatic pressure • Turgor pressure • Osmotic pressure normal plant cells after plasmolysis 5.8 Endocytosis and Exocytosis plasma membrane Exocytosis cytoplasm Endocytosis cytoplasm Endocytosis Pathways • Bulk phase • Receptor-mediated • Phagocytosis clathrin Figures 5.17, 5.18 Pages 92, 93 Membrane Cycling clathrin Exocytosis and endocytosis continually replace and withdraw patches of plasma membrane Figure 5.19 Page 93 Golgi body lysosome