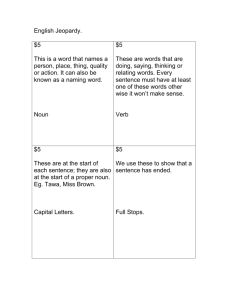
Synonyms - mspshg092010
advertisement
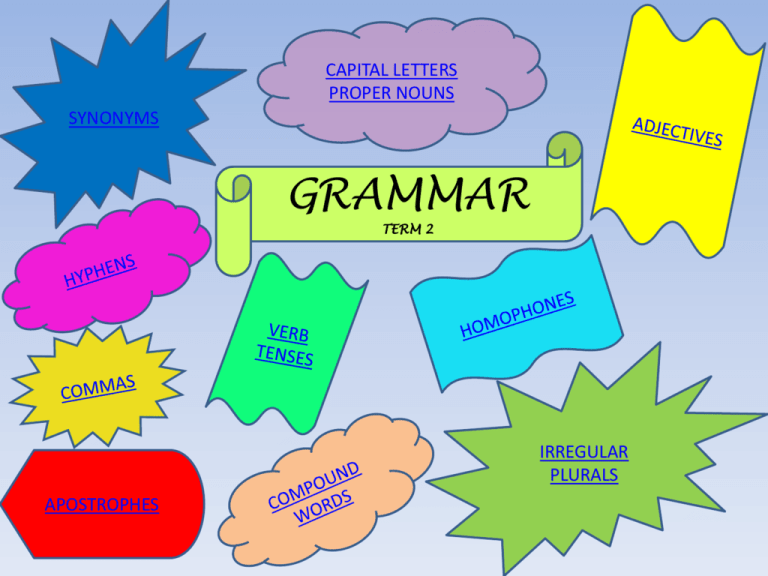
CAPITAL LETTERS PROPER NOUNS SYNONYMS GRAMMAR TERM 2 IRREGULAR PLURALS APOSTROPHES Synonyms Synonyms are words with the same or similar meaning. For example, joyful, elated, glad. 1. View the PowerPoint called Synonym-ppt listed on the page with the following link. http://languagearts.pppst .com/synonyms.html Complete the activities on the PowerPoint. Copy the sentences below into your Literacy books. Use a thesaurus (and your own knowledge!) to find three alternative words (synonyms) for the underlined word/s in each sentence. N.B. There may be more than one underlined word in a sentence. Set it out like this: The forest was scary. In your books write: The forest was frightening/terrifying/petrifying. 1.) The girl cried loudly. 2.) She was worried that she would not be invited to the party. 3.) Fiona walked to the park to meet her friends. 4.) Peter said, “No! I hate Brussels sprouts! I am not going to eat them!” 5.) Kim thought how nice her birthday cake was as she ate it with her family. 6.) Jessica told her friends how good the Black Hole at Alton Towers was. 7.) I was surprised when I won first prize at the raffle. 8.) Toby’s Grandma was very pleased with her birthday present. 9.) The large bulldozer held up all the traffic. 10.) The school trip promised to be an exciting one. Use http://thesaurus.com/ to complete the table of SYNONYMS beautiful inform brave predicament interesting marvelous mischievous dangerous CAPITAL LETTERS – PROPER NOUNS Capital Letters When do you use a capital letter? 1. A sentence always begins with a capital letter. 2. A proper noun, like a person’s name, begins with a capital letter. 3. A proper noun, like a place, begins with a capital letter. 4. Proper nouns, which are SPECIAL names, begin with a capital letter. (Christmas, Easter, June, Monday etc.) http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/baske tball/index.html Complete the following table. In each box, give an example of a proper nouns for each category. (Don’t forget to use a capital letter) A city A movie star A shopping centre A day A river A month A special holiday A country A state of Australia A book title A family member A mountain A desert A newspaper A magazine A nationality A brand of chocolate A bridge A song A make of car ADJECTIVES Adjectives are words that describe nouns or pronouns. They help make writing more interesting and clearer. Adjectives often compare the qualities of things. These are adjectives of degree. There are three adjectives of degree. •Positive – describes a quality of a person or thing. Will is a tall boy. •Comparative – makes a comparison between the qualities of two people or things. Jack is taller than Will. Superlative – shows the highest degree of difference compared to all others. Hamish is the tallest boy in our class. Where's The Adjective? An adjective is a word which modifies a noun. It describes the noun, or names one of the characteristics of a noun. For example, the following adjectives are underlined: red car, sweet apple, dirty water Circle the adjectives that describe the underlined noun or nouns in each sentence. (Words that you should circle are in italics.) Example: The small red shiny beetle scampered down the green leaf. 1. Ten puppies are playing in the tall, green grass. 2. Where is the small frying pan? 3. Sam has a blue racing bicycle. 4. The black kitten was playing with a small red ball. 5. Do you know the man in the black leather jacket? 6. I have seven coloured marking pens for school. 7. The city is big, dirty, and noisy. 8. Three beautiful birds searching for worms. 9. That is the biggest stuffed toy in the shop. 10. He ran through the wet muddy field. 11. Hand me the yellow plastic bowl. 12. The blue vase was broken by the naughty boy. 13. The black and white cat climbed the fence. 14. David has a red apple, but Sam has a green one. 15. Sam’s apple is sour. http://www.ngflcymru.org.uk/vtc/ngfl/english/monmouthshire/choose_ adj_monmouthshire.html IRREGULAR PLURALS Write the plural in the column below foot tooth ox louse goose deer fish octopus child man person leaf life wolf cactus Commas We use commas in two main ways Commas separate the items in a list. Sometimes these items are real things. E.g. I need some pens, pencils, paper and a calculator before I start my class. I must buy some eggs, milk, sugar and tea. Click on the links and complete the following worksheets. Sometimes these items are things you do, or places you go. E.g. Yesterday I went to work, played badminton, went to the pub and then went to bed. I'm going to spend my holiday walking on the beach, sleeping in the sun and reading my book. http://www.bbc.co.uk/ skillswise/words/gram mar/punctuation/com mas/worksheet.shtml Commas mark out the less important part of a sentence. This is a useful way to make your sentences more interesting by adding extra information. E.g. The car, which was parked by the light, had a dog in the back seat. This sentence is about the car and the dog, it's not about where the car was parked. Copy into your workbook. Tony, his mum's favourite, was given chocolate cake for tea. This sentence is about Tony eating chocolate cake. We don't need 'his mum's favourite' for the sentence to make sense, it's extra information. http://www.bbc.co.uk/skillswis e/words/grammar/punctuatio n/apostrophes/game.shtml Put in the appropriate apostrophes. 1. I cant go with you to Colins house. 2. Lets go to the Bears game on the weekend. 3. I dont think my dads hat will fit me. 4. The girls bathing suits need to be put in the dryer. (several girls) 5. Im going to head down to Clarks department store later. 6. Wheres the book I was reading, Im really enjoying it? 7. I put the dogs bones in the lower cupboard. (2 dogs) 8. I put the dogs bones in the lower cupboard. (1 dog) 9. Im going to my friends house to work on homework. 10. Jans clothes are always in style. 11. Buy your notebooks here and youll save money. 12. The cats whiskers are covered in milk. APOSTROPHES Rules for Using The Apostrophe The apostrophe has 2 functions: One is to show possession/ownership and the other is to show omission of letters or words. •1. An apostrophe shows ownership: John’s new shoes are red. •1a. These are the student’s books. Several books belonging to 1 student. •1b. These are the students’ books. Books belonging to a group of students. My 3 friends’ shirts are blue. More than 1 friend. The lions’ Den (More than 1 lion) Amos’ books (instead of Amos’s books) Sometimes a name ending on an s is given an apostrophe instead of an additional s and apostrophe as seen in the name Amos, typically both are correct. •1c. Add an apostrophe to the end of plural nouns that end in s: Boys’ hats. Players’ uniforms 2. An apostrophe is used in contractions when a word or letter(s) is missing: 2a. Don’t go outside. (Do not) I’ll finish my homework later. (I will – I’ll) COMPOUND WORDS A word formed when two or more words are joined. Each of the words must be a word that can stand alone. For example; sea + shore=seashore, rain + coat=raincoat, son-in-law HYPHENS Ambiguity – when the meaning of a sentence is not clear – is often caused by incorrect punctuation. Explain why each sentence is ambiguous, then punctuate the sentences so that the meaning becomes clear. 1. Man eating tiger destroyed. 2. For sale: a little used boat. 3. Two week holidays to be won! 4. Mountain holiday prices at rock bottom. 5. Beware of car chasing dog on M25. A hyphen is used to form new words beginning with the prefixes self, ex, great, all, and half. A hyphen is also used with suffixes such as free and elect. Examples: great-grandfather, half-baked, all-purpose, self-esteem, sugar-free A hyphen is used to make some compound words. Example: Matt was not well-known, even though he climbed Mt. Everest. Define each of the following so that their meaning is explicit. 1. yellow-bellied 2. even-tempered 3. tight-lipped 4. baby-faced 5. wide-eyed 6. light-footed 7. pig-headed 8. heavy-handed 9. hard-hearted 10. long-winded HOMOPHONES Homophones are words that sound the same but are spelt differently and have different meanings. Choose the correct homophone to complete this sentence. (a) The boy put shampoo on his (hare/hair). (b) Mum put some (flower/flour) in the cake mix. (c) James didn't have a very good (nights/knights) sleep. (d) A rabbit is a bit like a (hare/hair). (e) Tony got chased by a large (bare/bear). Choose the correct homophone to complete the sentences. (a) Lucy couldn't wait to (meet/meat) her friend. (b) Andrew (missed/mist) the bus. (c) The mouse got his (tale/tail) caught. (d) Glen has a long (wait/weight) for the bus. (e) The cat hurt its (pour/poor/paw). (f) The old man had no money, he was (pour/poor/paw). (g) "Could you (pour/poor/paw) the orange juice, please?" (h) Mark got a letter in the (mail/male). http://www.bbc.co.uk/skillswise/w ords/spelling/recognising/homoph ones/game.shtml Write the homophones for the following words; plane, right, see, there, which, where, be, for, here, knew, no, so, Explain the differences between these words. or / oar sail / sale saw / sore maid / made main / mane VERB TENSES To form the past tense of most verbs, add -ed. example: jump - jumped To form the present tense of most verbs, add -s or -es. examples: speak - speaks To form the future tense of most verbs, add the helping verb will before the main verb. example: fix - will fix http://www.bbc.co.uk/s killswise/words/gramma r/tenses/getting_the_rig ht_tense/game.shtml http://ww w.arcademi cskillbuilde rs.com/ga mes/viper/ viper.html Examples and rules for irregular verbs http://chompchomp.com/han douts/irregularrules01.pdf Underline the error and rewrite the sentences in perfect tense. Use your workbook.