Gas exchange - Our eclass community
advertisement

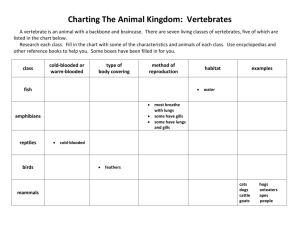
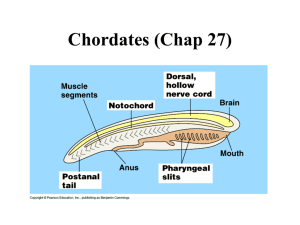
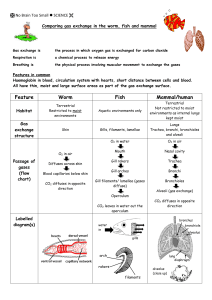
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS Biology ATAR Unit 2 Chapter 11 275-277 Keywords Tracheal system Spiracles Lungs Air sacs Alveoli Gills Diffusion Concentration gradient Counter-current system Making connections All multicellular organisms need systems for gas exchange The type of system an organism has is dependent its size and on the environment it lives in All systems have common characteristics that increase the efficiency of gas exchange GAS EXCHANGE Gas exchange in animals is by diffusion The 2 main gases exchanged is O2 into the body and CO2 out of the body A high concentration of CO2 is more dangerous to organisms than a low concentration of O2 Oxyge n Carbon dioxide GAS EXCHANGE SURFACES Characteristics of effective exchange surfaces: 1. 2. 3. 4. Large surface area to volume ratio Thin & permeable Moist – enables the dissolution of O2 for diffusion into the blood stream High concentration gradient is maintained across the membranes TYPES OF GAS EXCHANGE SYSTEMS System Animal Example Moist skin Adult amphibians Cnidarians Insects Arachnids Frogs Jellyfish Grasshopper Redback spider Tracheal system Lungs Mammals Reptiles Lungs with Birds air sacs Humans Lizards Chickens Gills Goldfish Crabs Tadpoles Fish Crustacean Juvenile amphibians MOIST SKIN CNIDARIANS Cnidarians are aquatic animals Gases continually diffuse across the membranes AMPHIBIANS (FROGS) Tadpoles have external gills Frogs rely on their lungs and their moist skin for gas exchange TRACHEAL SYSTEMS Insects have holes (spiracles) which lead into tubes (tracheas) The O2 diffuses through these from the outside air and CO2 leaves by diffusion in the opposite direction GILLS The amount of dissolved O2 in water is a lot less than it is in air Therefore, gills have a greater surface area as compared to the lungs of a similarly sized mammal Gills are highly convoluted structures with a very high surface area. Blood flows in the opposite direction to the water (counter-current) increasing the efficiency of gas exchange Gills rely on water flowing over them to ensure maximum O2 uptake Gills are the most efficient gas exchange system out of all 3 types of systems LUNGS WITH AIR SACS Birds have lungs with air sacs They are inflated and deflated by the muscles of the rib cage The air sacs force air through very fine tubes where the gas exchange takes place LUNGS Mammals and reptiles have lungs. The air travels: 1. In through the nostrils 2. Down the trachea 3. Into the alveoli of the lungs Gas exchange takes place in the alveoli Alveoli dramatically increase the surface area of the lungs