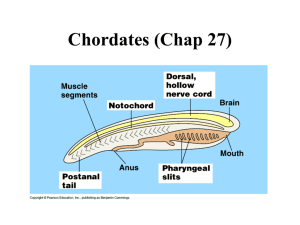
Ch.24 Fish
advertisement

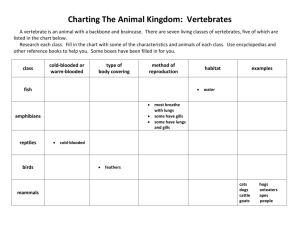
fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals Pouch lamprey, hagfish, and lamprey eel • Nervous system • Closed circulatory system –Heart ->ventricle->Aorta-> gills • Excretory • Respiration • Feeding • Reproduction: • A: Myxini• B. Chondrichthyes• C. Osteichthyes- • D. Petromyzontida- CLASSES MYXINI,PETROMYZONTIDA, SARCOPTERYGII Chondrichthyes and Actinopterygii Characterisitics Class Myxini Class Petromyzontida Examples Mouth Hagfishes Lampreys 4 pairs of tentacles Sucking mouth with teeth and rasping tongue Olfactory sacs Pharyngeal slits Open to mouth Blind sacs 5-15 pairs; one opening 7 pairs; separate openings Feeding Scavenge dead or dying fish; produce copious slime Parasitic or predatory; feed mainly on blood Characterisitics Examples Chondrichthyes Sharks, skates, rays Osteichthyes All bony fish Digestion Complete, lack pyloric Complete, have a pyloric cecum, have a cloaca (a cecum (used to increase common opening for the absorption in the intestine) reproductive, excretory and digestive systems) Respiration Gills Gills covered by an operculum (helps pump water across the gills) Skin Covered by placoid scales (feel sandpapery) Covered by cycloid or ctenoid scales Skeleton Cartilage endoskeleton Bony endoskeleton Circulation Closed, two chambered Closed, two chambered heart; 1-loop (from heart heart; 1-loop past gills to the rest of the body and back to the heart) Swim bladder (gas filled sacs that regulate buoyancy) Lacking Typically present Temperature regulation Ectothermic Ectothermic Lateral line system (used to Present Present Movement Paired fins (used for more precise steering and increase agility), heterocercal tail Paired fins, homocercal tail Reproduction Dieocious, internal Dieocious, variable fert.; fertilization, ovoviviparous, some are oviparous, some males have modified pelvic are ovoviviparous fins called claspers detect movement in the water)