Phylum Chordate
advertisement

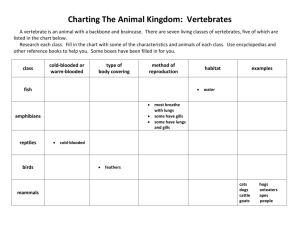
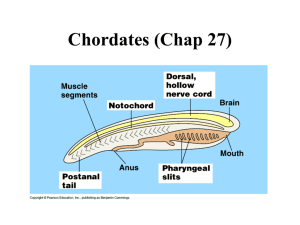
Phylum Chordata --Vertebrate chordates: fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals --Invertebrate chordates: tunicates and lancelets Characteristics (embryonic development) Dorsal hollow nerve cord Notochord—firm flexible supporting rod located just below the nerve cord Gill slits—paired opening along the pharynx Post anal tail…extends beyond the anus Endothermic Warm blooded..temp is controlled by internal processes Ectothermic Cold blooded..temp is regulated by external environment Three Subphylums 1. Urochordata --tunicates (sea squirts) --most adults are sessile, squirt water when disturbed 2. Cephalochordata Lancelets Can swim but prefer to stay buried in the sand Filter feeders 3. Vertebrata (humans) Animals with backbones Dorsal hollow nerve cord becomes the spinal cord and brain Notochord is the backbone Gill slits become other breathing organs Tails are kept in most vertebrate animals Six Classes 1. Agnatha --no jaw (jawless fish) --skeleton made of cartilage --snake-like body without paired fins (not good swimmers) Examples Lampreys—attach to other fish using their round mouth and its rasping parts (parasites) Hagfish—scavengers, move slowing through cold water using tentacles to locate dead and dying fish Hagfish Have you ever gone fishing? Tell me about your experience. OR Pick your favorite fish and describe it. Why do you like it. 2. Chondrichthyes Sharks, skates, rays General characteristics Skeleton mostly made of cartilage Have scales made of dentin Excellent sense of smell Lateral line picks up vibrations Sharks—torpedo shape body fertilization is internal and the eggs develop internally Young sharks are called pups Must keep moving to keep water flowing through gills Oily liver helps buoyancy Skates and Rays—basically benthic (bottom) lie and wait animals Have a tail which can cause pain Pectoral fins are expanded and they look like they are gliding in the water 3. Osteichthyes Characteristics Bony skeleton—bony fishes Swim bladder Scales Paired fins Operculum flap covering gills 2 chambered heart kidneys Page 608…Read the life cycle section Using complete sentences, explain the life cycle of a frog Compare and contrast the animals in the class chondrichthyes to the animals in the class osteichthyes. 4. Amphibians frogs, salamanders, toads, caecilians Spend part of their life in the water and part living on land Tadpole Frog Frogs Have a nictitating membrane over their eye…keeps eye moist in air and protects in the water Hear through a tympanic membrane (detect sound through air and water Digestive System Path of food Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, cloaca Undigested food along with products from the excretory system and reproductive system empty into the cloaca Respiratory Breathe using lungs Diffuse oxygen through skin (must stay moist) Tadpoles have gills for gas exchange Circulation Double loop circulation Three chambered heart Deoxygenated blood flows to the heart, then it is pumped to the lungs where it is oxygenated, then it flows back the heart to be pumped to the rest of the body Page 608 Metamorphosis Frogs are the only amphibian to go through this process Egg Tadpole…tail, gills, lives in water Frog…no tail,lungs,has legs, lives on land A froggie eats bugs. Tell me the pathway that the bugs will travel as they go from the froggie’s mouth to its anus. Look at the five pictures on page 804 List some adaptations that you see for these reptiles. Must have at least 5 5. Reptiles Ectothermic Egg-laying..soft, leathery shells Scaly dry skin..adaptable to life on land Internal fertilization Breathe with lungs Endoskeleton 3-chambered heart except crocodilians Kidneys remove wastes and absorb most of the water Shed skin Eggs are called Amniotic eggs b/c they have a fluid filled amnion sac which surrounds the embryo 6. Aves Feathers Contour feathers—have a stiff central barb Down feathers—short shafts, for insulation Oil gland at base of feather..waterproof Wing flow Bones are hollow to reduce density Fused collarbone and vertebra…furcula 4-chambered heart Endothermic (warm blooded) High metabolism (eat a lot!) Digestive system..crop (storage), gizzard (grinding…often contains stones) Unique respiratory system Anterior and posterior air sacs in addition to lungs Air flows in air sacs in only one direction (pg 810) Excretion..no urinary bladder Special glands around the eyes remove excess salts 7. Mammals Mammary glands..produce milk to nurse young Fur or hair Endothermic Well developed brains Internal fertilization…live birth Breathe with lungs Contain air sacs Diaphragm..muscle under lungs which helps breathing Examples… • Monotremes: mammal that lays eggs (duck-billed platypus • Marsupials: Kangaroo..give birth to small immature young that further develop inside mom’s pouch (Pg 829) • Placental: young develops more fully before birth Placenta..organ attached to mom and fetus Mammalian Teeth Page 823 Orders of Placental Mammals Page 830