Primary Economic Activity - Doral Academy Preparatory
advertisement

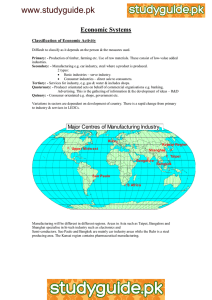
Economic Activities Economic Geography: the study of people’s livelihoods, how livelihood systems vary, & how they are interrelated to the environment & other people TYPES OF ECONOMIC LIVELIHOOD A. Categories of Economic Activity 4. “White-collar” information services 5. High-level decision making 3. “Service-sector” industries 2. “Value added” industries 1. Harvest or extraction Human Economic Activities Primary industry—those involved in extracting natural resources from the Earth. Secondary industry—processing stage, commonly called manufacturing, processing, or construction. Other three types all involve services of some sort, rather than the extraction or production of commodities. Tertiary: retail, wholesale, or personal/professional services Quaternary: information, research, management Quinary: executive decision makers B. Locational Factors for Economic Activities 1. Primary Economic Activities: -- must be located close to the resource Primary Economic Activity: Nga Trang, Vietnam Primary Activities: I. Subsistence Agriculture: for survival II. Commercial Agriculture: for profit – Extensive Agriculture • • – Intensive Agriculture • • – – Small labor input for large land area Relies on natural fertility of soil Large labor for small land area Use of machinery, pesticides, fertilizers, etc. The Green Revolution Urban Subsistence Farming III. Resource Exploitation: fishing, forestry, mining 2. Secondary Economic Activities Needs to be accessible to: - the resource - an energy source - a labor force - a market 3. Tertiary Economic Activities • proximity to the market is the most important locational factor for tertiary activities 4. Quaternary Economic Activities • access to telecommunications infrastructure & highly-skilled work force most important 5. Quinary Economic Activities • locationally tend to cluster