Chapter 5: The Structure of Matter
advertisement

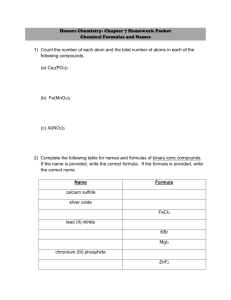
Objectives Determine the name of covalent compounds Determine the formulas of covalent compounds Naming Covalent Compounds Are named using different rules For two-element covalent compounds, we use numerical prefixes to tell how many atoms of each element are in the molecule Example: N2O4 Dinitrogen tetroxide Practice SF4 PCl3 N2O P2O5 CCl4 Writing Formulas for Covalent Compounds Step 1: Write down the symbols that match the element names Step 2: Write the value of any prefixes as the subscript for each corresponding element Practice 1. Tetraphosphorus decoxide 2. Selenium monoxide 3. Dioxygen difluoride 4. Sulfur hexafluoride 5. Dihydrogen monoxide 6. Nitrogen trihydride Chemical Formulas for Covalent Compounds A compound’s simplest formula is its empirical formula Empirical formulas tell us the smallest wholenumber ratio of atoms that are in a compound Example: H2O Different compounds can have the same empirical formula So we have to use molecular formulas for some compounds Empirical & Molecular Formulas Finding Molecular Formulas