Disability
advertisement

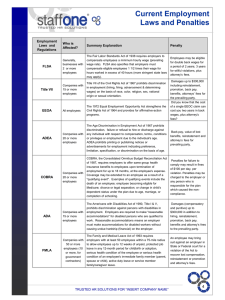
Introduction to Legal Issues in Human Resource Management Basic HR Issues to Consider when Creating New Ventures Modified from Marie Mitchell (2006), UN Lincoln, Advanced HR Management Terms: Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) Provide Americans an equal opportunity to compete for jobs for which they are qualified Regardless of race, age, gender, religion, national origin, or disability, Implies Evaluation of candidates for jobs based on characteristics that determine success and failure Fair and equal treatment on the job Terms: Discrimination Defined Giving an unfair advantage (or disadvantage) to the members of a particular group in comparison with the members of other groups Includes reverse discrimination Discrimination implies excluding someone unfairly Selection implies exclusion Key is to select non-discriminately Forms of Discrimination 1. Disparate Treatment: treating applicants or employees differently (e.g., discriminating) because of their membership in a protected class 2. Proved by Direct method: defendant admitting disparate treatment, Comparative evidence: others not in protected group treated differently Mixed-motives: plaintiff only needs to prove that protected class membership was a part of the reason for disparate treatment Adverse Impact: discrimination has an “adverse impact” on the protected group as a whole 4/5th Rule: adverse impact is indicated when less than 4/5ths of the percentage of total people within the population is not represented in the employees (see next slide) Adverse Impact: Example Federal Anti-Discrimination Laws Civil Rights Act of 1866 Civil Rights Act 1871 Gave all citizens right to enter into contracts No remedies for unjust treatment provided Gave individuals rights to sue if they felt deprived of rights guaranteed in Constitution or other laws Equal Pay Act 1963 Prohibits wage discrimination based on gender Equal pay for equal worth (equal skill, effort and responsibility under similar working conditions) Civil Rights Act (CRA, 1964), Title VII Prohibits discrimination in employment based on race, color, religion, sex and national origin Covers Private employers with 15+ employees State and local governments Private and public educational institutions Private and public employment agencies Labor unions with 15+ employees Joint labor/management committees that govern apprenticeship or training programs Foreign subsidiaries of U.S. organizations employing U.S. citizens Created the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) CRA (1964), Title VII (Cont.) 1972 Amendments Prohibit denial, termination or suspension of government contracts to employers sustaining an accepted AA program Affirmative Action (AA) Actions appropriate to overcome effects of past or present policies, practices or other barriers to EEO AA Plans Development, implementation and maintenance of special efforts to ensure workforce is representative of society where business operates Required for employers with 100+ employees and with $50,000+ in federal contracts Civil Rights Act (1991) Extended Title VII coverage to federal employees Allows for suing for compensatory and punitive damages Provided “extraterritorial enforcement,” protecting U.S. employees on overseas assignments Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA, 1967) Prohibits discrimination in pay, benefits or continued employment for those 40+, unless a BFOQ (bona fide occupational qualification) Prohibits mandatory retirement ages, except in cases of public safety (e.g., airline pilots) Amended by Older Workers Protection Act (1990) Prohibits discrimination of benefits and requires signing age discrimination waivers at layoff Pregnancy Discrimination Act (1978) Prohibits discrimination against pregnant employees In hiring or employment decisions (promotion) Employer cannot determine dates of leave Employer cannot provide health plans that do not cover pregnancy Requires any pregnancy to be treated as any other medical disability Does not require reinstatement to the same job Requires reinstatement to an equivalent job Immigration Reform & Control Act (IRCA, 1986) Covers Mandates 1. 2. 3. 4. All employers in U.S. All employees Employer cannot hire or continue to employ “unauthorized— illegal—aliens” Employers must verify the identity and work authorization of every new employee Employers may not discriminate based on citizenship or national origin provided workers are legal Certain illegal aliens must have amnesty rights (e.g., been pardoned) Regulatory body = U.S. Department of Labor Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA, 1990) Prohibits employers with 15+ employees from discriminating against a qualified individual with a disability Qualified individual – one who is able to perform essential functions of the job with or without accommodation Employer required to make “reasonable accommodations” for qualified, disabled, employees “Reasonable” means that it must not put an undue hardship on the employer Disability – a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities If person has an impairment If person has record of impairment If employer thinks person has impairment ADA (1990) (Cont.) 5 Implications for Employers 1. Any company open to public will have to be made accessible to those with physical disabilities 2. Expenses and “undue hardship” Reasonable accommodation for those qualified with disabilities Reasonable accommodation include but are not limited to: Making facilities readily accessible to/usable to disabled Job restructuring, modifying work schedules, reassignment to other position Acquiring or modifying equipment or devices, adjusting or modifying examinations, training materials or policies, and providing qualified readers or interpreters ADA (1990) (Cont.) 3. Pre-employment testing is permissible only if all employees are subjected to them and cannot be given until conditional offer of employment is made 4. Employee medical information must be kept separate 5. Drug-testing rules remain intact Family Medical Leave Act (FMLA, 1993) Covers private employers with 50+ employees Provides employees up to 12 weeks’ unpaid leave/yr for: Employee must have min. of 25 hrs/wk or 1,250 hrs/yr Birth, adoption or foster care of child w/in 1 year of child’s arrival Care for spouse, parent or child with serious health condition Employees own health condition prevents working Requires Continuation of group health coverage during leave Employee allow to return to same or equivalent job Other Federal Laws to Keep in Mind Law Brief Description Executive Order 11246 (1965) Prohibits discrimination of race, color, religion or national origin as condition of employment by federal agency, contractor or subcontractor with contracts of $10,000+; employers must maintain AA Program in each facility with 50+ employees Executive Order 11375 (1967) Amends E.O. 11246, prohibiting discrimination of sex Executive Order 11478 (1967) Amends E.O. 11246 and 11375, prohibiting discrimination based on political affiliation, marital status or physical disability Rehabilitation Act (1973) Federal contractors, who receive $2,500+ in federal contracts/annually and subcontractors must actively recruit qualified disabled individuals Vietnam Era Veterans Readjustment Federal contractors and subcontractors required AA Plan to Act (1974) ensure EEO for Vietnam-era veterans. Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act (1994) Regardless of size of organization, cannot discriminate on basis of person’s membership or potential membership in armed forces; must reemploy returning uniformed service members Regulating Agencies EEOC Regulates Many EEO Laws CRA (1964, 1991) and Title VII Equal Pay Act (1963) ADEA (1967) Pregnancy Discrimination Act (1978) ADA (1990) Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs Regulates Contract Compliance Executive Orders 11246, 11375 and 11478 Rehabilitation Act (1973) Vietnam Era Veterans Readjustment Act (1974) Guidelines to Employment Inquiries Guidelines to Employment Inquiries (Cont.) Guidelines to Employment Inquiries (Cont.) Guidelines to Employment Inquiries (Cont.) Responding to Claim of Unlawful Discrimination EEOC may Make determination w/o request for additional information Request additional information Hold a fact-finding conference Things to keep in mind with on-site investigation Negotiate mutually agreeable date and time for inspection Ask for description of investigation goals and try to prepare Review list of employees EEOC wants to talk to, observe or job/work areas they wish to see Designate company rep to attend all EEOC interviews of managerial employees