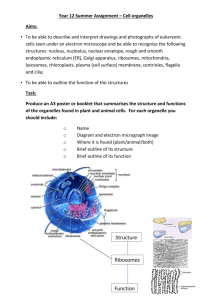
Plant Cell Structure and Function
advertisement

Plant Cell Structure and Function By Carragh Knapp Cell Structure (Key Features) Click the one you would like to know more about… Nucleus Nucleolus Mitochondria Golgi bodies Ribosomes Lysosomes Rough and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Microtubules * Plastids* Vacuole * Chloroplasts * *= [Click and then press spacebar] Inter-Relationships Nucleus and Nucleolus The Nucleus holds the genetic makeup or Chromosomes of the plant cell. Through a microscope, it also appears that there is another nucleus within the nucleus. This is the nucleolus and is made of a combination of RNA and protein. Back to Menu? http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell _nucleus.html Mitochondria and Golgi Bodies (apparatus) The Mitochondria is where respiration occurs. The Mitochondria requires oxygen and releases carbon dioxide as its waste. Golgi bodies help to move protein around the cell. They also assist in protein recognition. Back to Menu? Ribosomes and Lysosomes Ribosomes are the protein builders of cells. When they attatch themselves to the Endoplasmic Reticulum it is called Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum. Here protein molecules are created. Lysosome enzymes break down cell waste and foreign particles. This means that they are also responsible for digestion when food is absorbed. Back to Menu? Rough and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum breaks down fats and moves substances around the cell. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum is called that because it has Ribosomes attached to it. Enzyme proteins are created here. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum has no Ribosomes attached. Back to Menu? Microtubules, Plastids, Chloroplasts and Vacuoles Microtubules are made of protein and help define cell structure and cell movement. Plastids are membrane bound structures in plant cells. These include green chloroplasts which are in charge of carrying out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are the organelle responsible for food production. They create the sugars that are later broken down by Mitochondria. Vacuoles are bubbles in cells which are used for storage. They can also contain wastes to stop the cell from poisoning itself. Back to Menu? Cytoplasm and Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) The Cytoplasm is a watery solution which contains the cell organelles (e.g. Nucleolus, mitochondria etc.) The Plasma Membrane is like a bouncer. It controls what substances come in and out of the cell. Back to Menu? How The Organelles Work Together It is important for organelles to work interdependently if the cell is planning to survive. It is essential that a plant cell has every organelle, as they are so reliant upon each others functions. Below you can see how different organelles relate to and rely upon each other… Cytoplasm Cell solution which contains organelles Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Breaks down fats after they are absorbed Golgi Apparatus Substances transported around cell Plastids including Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are in charge of food production, they make sugar used by the Mitochondria for respiration Nucleus and Nucleolus Controls cell using genetic information (therefore relates to every organelle) Vacuoles -In plant cells a large water vacuole helps to keep cell shape -Can store waste Mitochondria Releases carbon dioxide as it’s respiration waste Ribosomes Protein building blocks Lysosomes -Breaks down cell waste -Digest food Microtubules Help to define cell structure and movement Cell Membrane Chooses what is absorbed, including food source Back to Menu?