BIOL 2401 STUDY POINTS CHAPTER 3 (Key) What are the three
advertisement

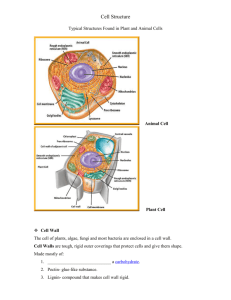
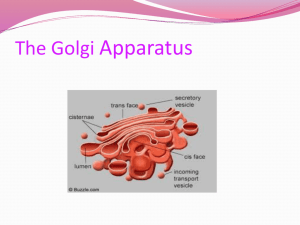
BIOL 2401 STUDY POINTS CHAPTER 3 (Key) 1. What are the three principle parts of a cell? Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus 2. What is the glycocalyx? It is layer formed beyond the outer layer of the plasma membrane by the carbohydrate portions of large molecules such as proteoglycans, glycoproteins, and glycolipids. It performs these functions: lubrication and protection, anchoring and locomotion, specificity in binding, and recognition. 3. Which cytoskeletal component helps form the structure of centrioles, cilia, and flagella? The microtubules help to form centrioles, cilia, and flagella. 4. What are the structural and functional differences between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum? Rough ER has attached ribosomes; smooth ER does not. RER synthesizes proteins that will be exported from the cell. Smooth ER is associated with lipid synthesis and other metabolic reactions. 5. What are the three general destinations for proteins that leave the Golgi complex? Some proteins are secreted from the cell by exocytosis, some are incorporated into the plasma membrane, and some occupy storage vesicles that become lysosomes. 6. Write the steps of protein synthesis. What is the “Cis” face and the “Trans” face of the Golgi complex? 1 A gene on DNA produces messenger RNA, the template for protein synthesis. 2 The messenger RNA =leaves the nucleus and attaches to a free ribosome in the cytoplasm, or a fixed ribosome on the RER. 3 Proteins constructed on free ribosomes are released into the cytoplasm for use within the cell. 4 When a protein is synthesized on fixed ribosomes, it is threaded into the hollow tubes of the ER where it begins to fold into its 3dimensional shape. 5 The proteins are then modified within the hollow tubes of the ER. A region of the ER then buds off, forming a transport vesicle containing the modified protein. 6 The transport vesicles move the proteins generated in the ER to the cis face (“receiving side”) of the Golgi apparatus. The transport vesicles then fuse with the Golgi apparatus, emptying their contents into the flattened chambers called cisternae. 7 Multiple transport vesicles combine to form cisternae on the cis face. Once inside the Golgi apparatus, enzymes modify the arriving proteins and glycoproteins. Further modification and packaging occur as the cisternae migrate forward the trans face (“shipping side”), which usually faces the cell surface. 8 On the trans side, different types of vesicles bud off with the modified proteins packaged inside. One type of vesicle becomes a lysosome, which contains digestive enzymes. 7. Where does transcription occur? Where does translation occur? Transcription occurs in the nucleus. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm. 8. Will a 2% solution of NaCl cause hemolysis or crenation of RBCs? Why? A 2% solution of NaCl will cause crenation of RBCS because it is hypertonic. 9. During which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? DNA replicates during the S pahse of interphase of the cell cycle. 10. When does cytokinesis begin? Cytokinesis begins with the formation of a cleavage furrow and continues through telophase. Critical Thinking: Marathon runners can become dehydrated due to the extreme physical activity. What types of fluids should they consume in order to rehydrate their cells? In order to restore water balance to the cells, the runners need to consume hypotonic solutions. The water in the hypotonic solution will move from the blood, into the interstitial fluid, and then into the cells. Plain water works well; sports drinks contain water and some electrolytes (which may have been lost due to sweating) but will still be hypotonic in relation to the body cells.