File

W ELCOME !
DO NOW…
What are civil liberties?
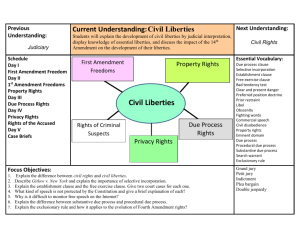
C
IVIL
L
IBERTIES
The individual freedoms guaranteed in the Bill of
Rights
They are primarily concerned with protecting citizens from too much government control
B ILL OF R IGHTS – T HEN AND N OW
The Bill of Rights protects freedoms at a national level, but these freedoms were not necessarily guaranteed in some state constitutions
In the case of Barron v. Baltimore (1883), the
Supreme Court ruled that states could not be forced to uphold the Bill of Rights if it conflicted with their state constitution
C ONT .
In Gitlow v. New York ( 1925), the Supreme Court reversed its earlier decision, citing the Fourteenth
Amendment as reason to enforce states’ protection of the civil liberties listed in the First Amendment
Gitlow v. New York (1925) began a tradition called the incorporation doctrine, by which the Supreme
Court has gradually ensured the protection of most freedoms listed in the Bill of Rights from state infringement
F REEDOM OF R ELIGION
First Amendment prohibits Congress from making laws establishing any religion in conjunction with the government [establishment clause]
Some critics interpret the clause loosely: The government should not favor one religion over another in its policies
Others, including Thomas Jefferson, argue that the establishment clause endorses the separation of church and state
F REEDOM OF R ELIGION
This clause is at the center of the debate over
Prayer in school
Federal funding of private religious schools
Pledge to the flag
Posting the ten commandments
What do you think about each of these issues?
F REEDOM OF R ELIGION
Federal funds may be used to construct school buildings and to provide administrative and academic supplies, but not to endorse religious teachings
Student religious groups cannot be denied access to school buildings for the purpose of meeting or worship
The Court has upheld that the government cannot infringe on people’s beliefs, but it can regulate religious behavior to some degree
State laws can ban religious practices that conflict with other laws, but they cannot forbid religious worship itself
F REEDOM OF E XPRESSION
Speech
Courts grapple with the definition of “speech”
Political protests and picketing protected by the First Amendment
But libel, pornography, and fraud are not
The Constitution forbids prior restraint, or government censorship, of the press
Prior restraint is granted in situations where national security might be compromised
LIBEL
The publication of false or malicious statements that damage someone’s reputation
F REEDOM OF E XPRESSION
Assembly
Includes the right to protest, picket, or hold a demonstration
The right to establish groups of people with similar political interests, from political parties to the KKK, is protected under the First Amendment
S EARCHES AND S EIZURES
The Fourth Amendment protects citizens from unreasonable searches and seizures
Police investigators cannot search private property without a search warrant issued by a court unless there is reason to believe that the evidence will disappear or be destroyed or removed in the meantime
The police cannot arrest someone unless there is probable cause to believe that he or she is guilty
The exclusionary rule prevents prosecutors from using evidence acquired through unreasonable search and seizure
S ELF -I NCRIMINATION
The Fifth Amendment protects people from being forced to supply evidence against themselves
Because a person is innocent until proven guilty, the prosecution is responsible for proving a defendant’s guilt
R
IGHT TO
C
OUNSEL
The Sixth Amendment guarantees that all accused persons tried in a federal court have the right to be represented by an attorney
C
RUEL AND
U
NUSUAL
P
UNISHMENT
Prohibited by the Eighth Amendment, though the term is not clearly defined in the Bill of Rights
R IGHT TO P RIVACY
Not specifically guaranteed by the Bill of Rights, but the Supreme Court has interpreted the first ten amendments to imply this right
T
HE
R
IGHT TO
P
RIVACY
T
HE
R
IGHT TO
D
IE
In 1997, the Court ruled that there was no constitutional right to assisted suicide.