Physical & Chemical Properties
advertisement

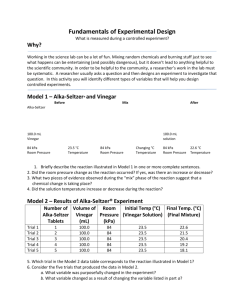
Messana Every element on the Periodic Table has it’s own set of physical & chemical properties, that is what makes their “personalities” unique!!! Property Is a description of an object The tree is GREEN If struck by lighting, the tree could catch FIRE (BURN) The tree is TALL What is a Physical Property? A characteristic of an element or substance that can be observed or measured without changing its identity or its structure Use your 5 senses OR scientific measurements to describe or measure… Physical Properties Are determined by the use of the . senses They are a description five of an object. Examples of Physical Properties Color Smell Taste Hardness State of Matter Boiling, Freezing, or Melting Point Examples of Physical Properties Density Mass Volume Malleability (the ability to be molded) Solubility (the ability to be dissolved) What is a Physical Change? A change that takes place without changing the identity or structure of the element or substance EXAMPLES: Dissolving Phase change (change between solid, liquid, or gas) Changing shape Examples of Physical Changes Change in size, shape, or color Pencil shavings Torn Paper Crushed ice Sugar dissolved in water Painting a wall VOCABULARY for INQUIRY STATIONS: Solubility Melting Point Boiling Point Magnetism Conductivity Malleability Density LET’S VISIT SOME STATIONS! Directions: Please go to assigned station and using the STATION VOCAB please decide which PHYSICAL PROPERTY represents the station and complete your PHYSICAL PROPERTY CHART & QUESTIONS! LET’S DO THIS LIL DARLINGS!! DENSITY Mass per volume of a material, or how much stuff is packed together in an area. SOLUBILITY A measure of how much of a substance dissolves in a given amount of another substance. MELTING POINT The temperature at which a solid changes to a liquid. MAGNETISM A force of attraction or repulsion that exists between like and unlike poles. The ability to be MALLEABILITY hammered, shaped, or rolled into thing sheets. Most metals are malleable. CONDUCTIVTY The ability of a material or substance that allows electricity or heat to flow through it easily. Most metals are good conductors. BOILING POINT The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas. SPECIFIC HEAT The amount of heat or energy needed to raise 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius (1C). What is a Chemical Property? A characteristic that gives a substance the ability to change into a new substance…BUT the chemical change has to be happening to see the chemical properties! What is a Chemical Change? A change that results in the production of a new substance and cannot be reversed. EXAMPLES: Burning Rusting Cooking Evidence of a Chemical Change/Reaction: Color changes – (color appears or disappears) Temperature changes Gas/gas bubbles produced Fire/explosion Precipitate is formed – a solid forms out of 2 liquids Examples of Reactivity… Metals Reacting to Being Burned http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d8hpUtRnsYc Physical Vs. Chemical Foldable Match each word in the word in the word bank with the correct definition… Then, decide whether each pair represents a physical or chemical property and put them on the correct side of your foldable under “Examples of Physical Properties:” or “Examples of Chemical Properties:” Hint: There are 8 Physical examples & 4 Chemical examples…CHECK BEFORE YOU PASTE! CHEMICAL REACTIVITY The ability of a material or substance to react with another material or substance and form something entirely new or different. TOXICITY The degree to which a chemical can harm an organism. FLAMMABILITY The ability of a material or substance to burn or start on fire easily. REACTIVITY WITH OXYGEN The ability of a material or substance (usually metals) to react with oxygen and cause them to rust, tarnish, or combust, spark or create a flame or light. Property or Change? THINK, GROUP, SHARE… Explain the difference between a property and a change. Physical or Chemical? THINK, GROUP, SHARE… Explain how you know the difference between a physical change and chemical change? What were those 5 helpful hints that I gave you to identify a chemical change? What were the 5 Things that give you a hint that a chemical change/reaction has occurred? Color changes – (color appears or disappears) Temperature changes Gas/gas bubbles produced Fire/explosion/flame/light produced Precipitate is formed – a solid forms out of 2 liquids Labs to Examine Chemical Changes Mini Lab 1: Make your prediction based on the items you see the teacher has… Watch closely…keep watching! Write your observations What was your “hint” that a chemical change occurred? FRIENDLY REMINDERS!! **Anyone sensitive to strong odors? Let me know if any of the odors are bothering you at any point during the labs today! **Absolutely none of the lab chemicals should come in contact with your mouth, eyes, or be breathed deeply!! GROUP 1 = SINK 1 GROUP 2 = SINK 2 GROUP 3 = SINK 3 ETC… GROUP 7 & 8 = SHARE A SINK USE YOUR PLASTIC BIN TO CATCH ANY SPILLS, FOR EXAMPLE WHEN YOU POUR VINEGAR INTO YOUR GRADUATED CYLINDER DO IT OVER THE BIN! Group Roles Leader: Reads the directions for each lab, keeps group on task and following directions Materials/Clean Up: collects, returns, cleans and disposes of materials Data Discussion Leader: Ensures there is a conversation about each data table to share information. Quality Management: Ensures every student has detailed quality answers written in complete sentences using scientific language & turns their lab guide in! Mini Lab 2: Send your materials person to get a cup of milk and a cup of vinegar, and a stir stick Pour the milk into the vinegar and stir it like you mean it! Observe and record any changes that occur at this time. Let this one sit on your table to see if there is any change by the time class ends. Mini Lab 3: Send your materials person up to pick up a ziploc bag with baking soda in it for each group Use the graduated cylinder to measure about 30 mL of vinegar Add the 30 mL of vinegar to the baking soda in the bag and SEAL THE BAG IMMEDIATELY Observe and record any changes that occur. Rinse your GRADUATED CYLINDER and throw away the ziplock bag ONCE YOU HAVE DUMPED THE CONTENTS DOWN THE DRAIN Mini Lab 4: Send your materials person up to get a MYSTERY test tube for each group member Use the eyedroppers to add an eyedropper full of the cabbage juice (purple liquid) to each test tube…DO THIS ONLY ONCE Observe and record any changes that occur WAIT FOR FURTHER INSTRUCTIONS!!! Rinse your test tubes and return it to the test tube rack. Flush your eyedroppers with water. Rinse your bin & dry it! Clean up any spills at your group! Mini Lab 5: Send your materials person to the sink to get approximately 5 ml of water in your graduated cylinder Put the water into your film canister & close the lid! Break one Alka-Seltzer tablet in half and hold it up in the air! ONCE WE ARE OUTSIDE… Put the Alka-Seltzer tablet into the film canister and snap the lid TIGHTLY QUICKLY put the canister on the ground CAP SIDE DOWN AND STEP BACK! Your lab station should be clean and your bin should contain all of the supplies it did when you started! Clean, dry plastic bin 1 graduated cylinder 1 bottle of vinegar 1 small beaker of cabbage juice 2 pipettes (eyedroppers) 1 packet of Alka-Seltzer 1 film canister What about the milk & vinegar? Something to try at home http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VFvik_THcNQ Check for changes in Mini Lab 2 – then pour your “new” substance down the drain and throw the cups and stir stick in the trash. Let’s Take a Look at the Lab… Quality Management: Ensures every student has detailed quality answers written in complete sentences using scientific language & turns their lab guide in! Stop using the word “it” – what is “it?” use the vocabulary/explain with detail SOME COMMON ERRORS: The 2 liquids, the milk and the vinegar, formed a precipitate…instead of it precipitated/it was precipitating – what does that mean? Is dissolving chemical or physical? Let’s Take a Look at the Lab… Question #2 on the back – some examples of good answers were: In the beginning we didn’t know what would happen in Mini Lab 2, but it greatly displayed how this relationship between properties and changes because you had to mix the milk and vinegar together before their properties could react and cause them to form a precipitate which was the chemical change. For experiment #4, we had to pour the cabbage juice into the mystery liquid to see it undergo the color change. The color couldn’t change without mixing the two liquids allowing you to see the chemical property through the chemical change. Physical Vs. Chemical Change Examples From the lab guide… From the homework… Whiteboard Quiz – Physical or Chemical? Number your whiteboard 1-10 You must get at least 9 correct to get a ticket 1. Physical or Chemical? Freezing water… 2. Physical or Chemical? Chopping Wood… 3. Physical or Chemical? Dissolving salt in water… 4. Physical or Chemical? Crumpled paper… 5. Physical or Chemical? Burning Wood… 6. Physical or Chemical? Melting Gold… 7. Physical or Chemical? Dying Easter eggs… 8. Physical or Chemical? Boiling Water… 9. Physical or Chemical? Frying chicken… 10. Physical or Chemical? Tarnish on the Statue of Liberty… Whiteboard Quiz Part 2 – Which Property? Number your whiteboard 1-10 You must get at least 8 correct to get a ticket 1. Which Property? The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas. 2. Which Property? Mass per volume of a material, or how much stuff is packed together in an area. 3. Which Property? The ability to be hammered, shaped, or rolled into thin sheets. Most metals have this quality. 4. Which Property? The ability to start on fire or to burn. 5. Which Property? The amount of heat or energy needed to raise 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius (1C). 6. Which Property? A measure of how much of a substance dissolves in a given amount of another substance. 7. Which Property? The temperature at which a solid changes to a liquid. 8. Which Property? The ability of a material or substance to react with another material or substance and form something entirely new or different. 9. Which Property? The ability of a material or substance that allows electricity or heat to flow through it easily. Most metals have this property. 10. Which Property? The degree to which a chemical can harm an organism. Fill in the video guide for a quiz grade!! www.studyjams.com Physical & Chemical Changes of Matter