Factors Market
advertisement

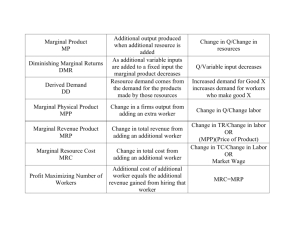
Factors Market Part 1 Factors of Production • Factors, Resources, Inputs – Land – Labor – Capital – Entrepreneurship Perfectly Competitive Labor Market • Households = Supply • Firms = Demand • Derived Demand – Product Market Demand – Shifts Labor Market Demand Perfectly Competitive Market and Firm MPP and MRP • MPP- marginal physical product – Additional output from additional unit of a resource – Change in TP from one more unit of resource • MRP- marginal revenue product – – – – Additional revenue from additional unit of resource Change in TR from one more unit of resource MPP X MR= MRP MPP X Price = MRP (in a perfectly competitive product market) MRC • Marginal Resource Cost (MFC=Marginal Factor Cost) • Additional cost from one more unit of resource • For labor, this is the wage • Perfectly Competitive Labor Market – Firms are wage takers – MRC (MFC) is perfectly elastic Tomorrow’s Quiz • Derived Demand • MRP • MFC (MRC) • Monopsony Extra Credit: Cost minimizing and Profit maximizing combination of resources (open packet) Monopsony Cost Minimizing Combination of Resources at a Given Level of Output • MPP/$ of Labor = MPP/$ of Capital – $ = MRC Example • MPP last unit of labor = 5 • MPP last unit of capital = 8 • Labor MPP/$ = .5 Wage rate (MRC)= $10 MRC = $16 Capital MPP/$ = .5 Optimal Combination (Profit Maximizing) of Resources • MRP/$ of Labor = MRP/$ of Capital= 1 – $ = MRC – Example • MRP last unit of labor = $10 • MRP last unit of capital = $16 • Labor MRP/$ = Capital MRP/$ = 1 Wage rate (MRC)= $10 MRC = $16 Perfectly Competitive Market and Firm • Supply = Marginal Resource Cost (MRC) • Demand = Marginal Revenue Product (MRP) • Profit-Max Q of Labor: MRP=MRC What’s Left • 4-6 Factors Market • 7-14 Government and Market Failure • 19/20 Bull's-eye Physical Challenge On to MACRO Year in Review • • • • • • • Michael Brown and Eric Garner June SCOTUS decision David Sweat and Richard Matt Refugee Crisis- most accepting country SC Church shooting town US visit Former Pat pleads guilty Perfectly Competitive Firm • MRP>MRC- hire more • MRC>MRP- fire some 11. Under what conditions is a firm’s MRP of labor curve the same as its demand curve for labor? • If firm hires in perfectly competitive resource market MRP Change in TR with one additional unit of an input (labor) • PC product market may use – MRP = Product Price X MPP • Monopolist in Product Market MUST use – Change in TR Monopolist and Perfectly Competitive Labor Market • Monopolist must drop the product price to sell more. • Monopolist must drop price when hiring more workers. • MRP is downward sloping due to decreasing MPP and decreasing price. • Must use change in TR to calculate MRP. • CANNOT multiply price and MPP because price is NOT MR! Individual Supply of Labor Curve • Trade-Off between work and leisure Individual Supply of Labor Curve • Trade-Off between work and leisure Minimum Wage and Labor Unions Minimum Wage in PC Labor Market? Unions • Collective Bargaining • _________ of workers • Clayton Antirust Act (1914) Unions in PC Labor Market? Unions and Monopsonistic Labor Market? Unions and Monopsonistic Labor Market • Bilateral Monopoly – One buyer, One seller – Outcome is difficult to predict Minimum Wage with Monopsony in Labor Market? Combination of Resources • Cost-Minimizing – MPPL/MFCL = MPPC/MFCC • Profit- Max – MRPL / MFCL = MRPC / MFCC = 1 Other Factors • • • • Labor = Wage Capital = Interest (that’s it until macro) Land = Rent Entrepreneurship- profit Land (Natural Resources) Economic Rent • Term originally only applied to land • Payment for land above price necessary for land to be made available • A decrease in the payment for land will not reduce the quantity of land available for rent. Economic Rent- modern • Payment for any factor above price necessary for that factor to be employed • A decrease in the payment for the factor will not reduce the available supply of the factor Economic Rent- in other words • Payment for/to any factor above the payment required by its owner Wage Determinant • Productivity *American worker overseeing mechanized assembly line *Foreign worker hand painting a decoration Wage Differential • Skills/Knowledge – Limits supply • MRP • Risk • Access Human Capital • Investment to improve skills and productivity of labor • Self or Firm • High wage jobs OFTEN include large human capital investments *Profession/Unions often push for high human capital requirements.