Essential graphs for AP Microeconomics
advertisement
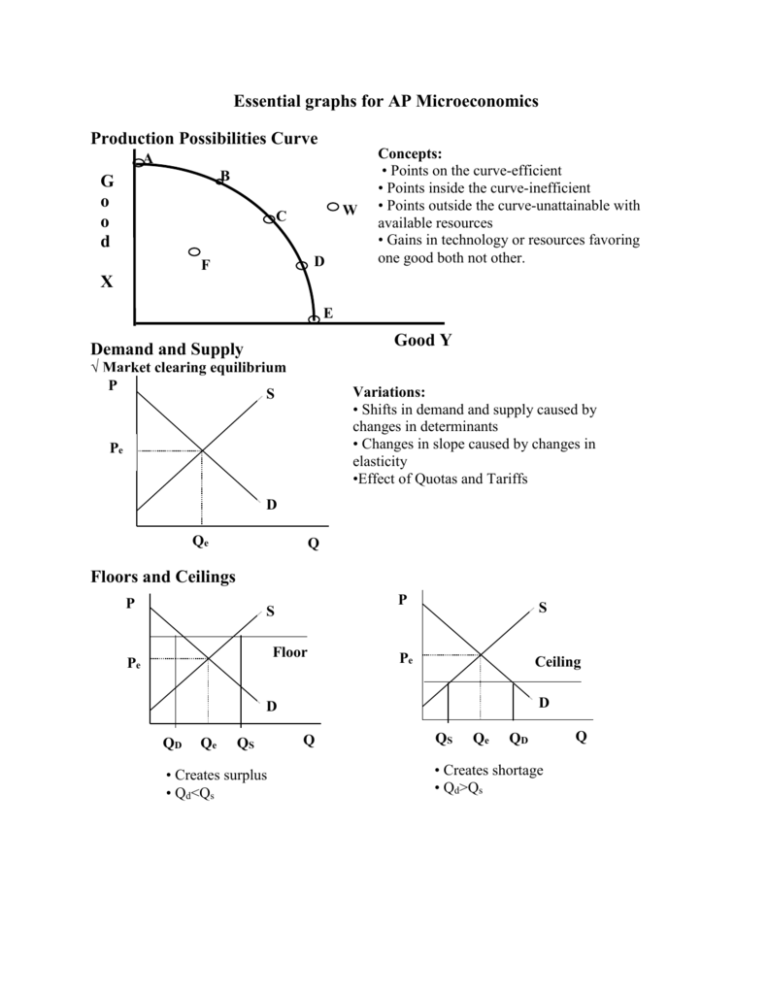
Essential graphs for AP Microeconomics Production Possibilities Curve A B G o o d W C D F X Concepts: • Points on the curve-efficient • Points inside the curve-inefficient • Points outside the curve-unattainable with available resources • Gains in technology or resources favoring one good both not other. E Good Y Demand and Supply √ Market clearing equilibrium P S Variations: • Shifts in demand and supply caused by changes in determinants • Changes in slope caused by changes in elasticity •Effect of Quotas and Tariffs Pe D Qe Q Floors and Ceilings P P S Floor Pe S Pe Ceiling D D QD Qe QS • Creates surplus • Qd<Qs Q QS Qe QD • Creates shortage • Qd>Qs Q Consumer and Producer Surplus Consumer surplus S P Pe Producer surplus D Qe Effect of Taxes Q A tax imposed on the BUYER-demand curve moves left • Elasticity determines whether buyer or seller bears incidence of tax • Shaded area is amount of tax • Connect the dots to find the triangle of deadweight or efficiency loss. Price buyers pay P Dead Weight Loss S Price w/o tax Price sellers receive D1 D2 Q A tax imposed on the SELLER-supply curve moves left • Elasticity determines whether buyer or seller bears incidence of tax • Shaded area is amount of tax • Connect the dots to find the triangle of deadweight or efficiency loss. Price buyers pay S2 Dead Weight Loss P S1 Price w/o tax Price sellers receive D1 Q Purely Competitive Product Market Structure Long run equilibrium for the market and firm-price takers Allocative and productive efficiency at P=MR=MC=min ATC P MC P S Pe AC MR=D=AR=P Pe D Qe Q Qe Q Variations: • Short run profits, losses and shutdown cases caused by shifts in market demand and supply. Imperfectly Competitive Product Market Structure Monopoly Market Structure Single price monopolist-price maker Earning economic profit P Natural Regulated Monopoly Selling at Fair return ( Qfr at Pfr) Dead Weight Loss MC P MC ATC P Pm ATC PFR D Ec Profit Q PSO D QFR QSO Qm Q MR Q MR Monopolistically Competitive Market structure Long run equilibrium where P=AC at MR=MC output MC P Variations: • Short run profits, losses and shutdown cases caused by shifts in market demand and supply. ATC PMC D Qmc MR Q Pure Competition Resource Market Structure Perfectly competitive Labor Market-Wage takers Firm wage comes from market so changes in labor demand do not raise wages. S Wage Rate Wage Rate Wc S=MRC Wc D= ∑ mrp’s DL=mrp Qc Labor Market Quantity Quantity qc Individual Firm Variations: • Changes in market demand and supply factors can influence the firm’s wage and number of workers hired. Imperfectly competitive market structure-Wage makers Quantity derived from MRC=MRP (Qm Wage (Wm) comes from that point downward to Supply curve. MRC Wage Rate S b Wc a Wm Qm Externalities No Externality P MRP c Qc Q Negative Externality MPC 2 MSC P Pe MSC Pe MSB Qo MSB Q Qo Qe Q Tax, direct controls, lawsuits, Coase theorem, market for externalities Positive Externality P MSC Pe MPC P MSC2 MSB 2 Pe MSB MPB Qe Qo Subsidy to buyer Q Qe Qo Subsidy to Seller Q