History of Astronomy
advertisement

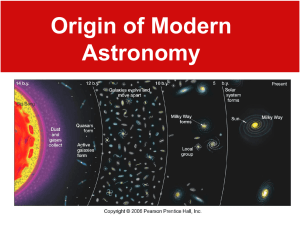
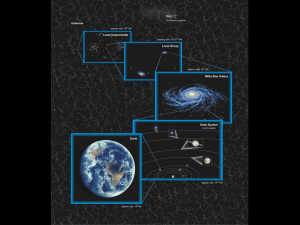
History of Astronomy How have ideas about the solar system and our place in it changed? Egyptians Saw patterns in the Sun, moon, and Venus Called the sun “Ra” (Sun god) – rode in his boat across the sky daily Developed 365 day year solar calendar Ra (on right) Greece Eudoxus, born 400 B.C. saw objects that moved in sky called planets, sun, and moon “wanderers” Earth motionless and at the center of universe Ptolemy, AD 140 Leading astronomer “geocentric” theory – earth is center of universe. Lasted for 1400 years. Ptolemy “epicycles” Arabs Caliph Harun-al-Rashid, ruler Scholars translated Greek texts into Arabic and preserved in “House of Wisdom” library – in Baghdad Measured positions of stars and planets with fine instruments, astrolabe, can perform calculations Named the red giant Betelgeuse, in Orion 325 light years away Betelgeuse – “shoulder” Orion constellation Poland Copernicus – 1540 First to suggest “heliocentric model” – sun is center of universe Objects orbit sun in perfect circles Still not a perfect model Copernicus from book De Revolutionibus The English version… What do you think? Why do you think it was difficult for people to accept a heliocentric model (sun centered) over the geocentric model (Earth centered)? Geocentric model Heliocentric model Denmark Tycho Brahe – 1576 Collected data of position of planets for 20 years Able to make accurate predictions of positions without telescopes Had own “Tychonic Universe” – combination of Ptolemy and Copernicus Earth is stationary Believed in circular orbits Tychonic Universe Why the Circles? Why do you think these astronomers believed in circular orbits? Kepler Works with Tycho – after Tycho’s death, Tycho’s family sued to recover instruments and books of observations Why? Kepler was a Copernican, and they knew he wouldn’t follow the Tychonic system Kepler kept the books! Began to study motion of Mars … Kepler Elliptical orbits Kepler’s First Law of Planetary Motion Orbits are elliptical (oval shaped), sun is at the focus Kepler’s Second Law of Planetary Motion A line from a planet to the sun sweeps over equal areas in equal times Planets travel at different speeds – due to pull of gravity Closer to Sun, moves faster… Why? Same time, moves slower Kepler’s Unanswered Question What keeps planets in orbit? Galileo Galilei Born in 1564 Supports Copericus’ theory of heliocentric universe Used telescope to observe: surface of Moon – was not perfect (like Ptolemaic model) Phases of Venus Milky Way was made up of many stars Moons of Jupiter Galileo Moon surface Phases of Venus Isaac Newton Born in 1654 (year Galileo dies) Three Laws of Motion Review from exam! These laws help us understand orbital motion 1st law – 2nd law – 3rd law – Newton answers Kepler’s Question… What keeps planets in orbit? Tying it all up… Myths See patterns Ptolemy Copernicus Kepler Galileo Newton Homework Timeline – list at least four models of relationship between sun and planets. Include: dates, astronomer, model Read – Chapter 16.1: pp. 526 – 530.