File
advertisement

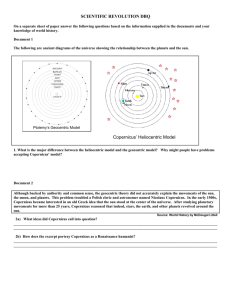
HISTORY OF ASTRONOMY Section 10.1 – Early Models of the Universe E V E RY S T O RY H A S A BEGINNING…. If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants. - Sir Isaac Newton (1642 – 1726) THE GREEKS:ARISTOTLE, PTOLEMY AND GEOCENTRISM A R I S T O T L E ( 3 8 3 – 3 2 2 B. C. ) A famous Greek philosopher, one of the first people to leave a written record of their thoughts about the solar system. His observations were made with the naked eye. This included the sun, the moon, the stars, and the planets. It would be almost two thousand years before telescopes would be invented! A R I S T O T L E ( 3 8 3 – 3 2 2 B. C. ) Important contributions: 1. The earth is a sphere. Aristotle observed a curved shadow on the moon and figured the earth must be casting the shadow. A R I S T O T L E ( 3 8 3 – 3 2 2 B. C. ) Important contributions: 2. He placed the earth at the centre of the universe because patterns in the stars did not seem to change. This resulted in the geocentric model of the universe defined below. GEOCENTRIC MODEL A model of the universe DRAW MODEL ON that places earth at the centre BOARD with the Sun, moon, planets and stars revolving around the earth. GEOCENTRIC MODEL The geocentric could not account for the apparent movement of the planets. For example, Mars seemed to change directions in a looping pattern which could not happen in Aristotle’s model. PTOLEMY (83 – 168 A.D.) Ptolemy attempted to explain the movement of planets by adjusting Aristotle’s model and making it more complicated! PTOLEMY (83 – 168 A.D.) Important contribution: 1. Suggested that planets move in epicycles as they orbit the earth. (DRAW DIAGRAM) NICHOLAS COPERNICUS Aristotle and Ptolemy’s model was accepted for centuries. It wasn’t until the 1500’s that people including Nicolas Copernicus began to challenge the Geocentric Model. Copernicus still only had his eyes to overserve the sky. H E L I O C E N T R I S M : T H E C O N T ROV E R S Y Important Contribution: He explained the motion of the planets by placing the sun at the centre of the universe. This was called the heliocentric model. HELIOCENTRIC MODEL Heliocentric Model: A model of the universe that places the Sun at the centre, with the earth and planets revolving around the sun. This is shown in the image below: Unfortunately, Copernicus was unwilling to present his theories because it went against the teachings of the church, which supported the geocentric model. His ideas would have been treated with persecution and possibly death by burning at the stake! Copernicus decided to keep his theories to himself until he was dying, at which point he published his ideas in a book. GALILEO GALILEI (1564 – 1642 A.D. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NMM8vx9vDiE A MARTYR IS BORN…ALMOST Galileo was forced to take back his theories in order to avoid being burned at the stake. JOHANNES KEPLER As Galileo was resting in house arrest, Johannes Kepler was working to prove Copernicus theory once and for all. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a19LTnXkyVQ KEPLER’S CONTRIBUTIONS Realized that all planets move in ellipses with the sun located at one focus. The time it takes a planet to revolve around the sun is related to how far away from the sun it is located. (DRAW ELLIPSE DIAGRAM) SIR ISAAC NEWTON Considered to be one of the most influential scientists to have ever lived. Important Contribution: • Used math to show that gravity keeps planets in orbit. TECHNOLOGY I) Stone Circles Hardly “technology” by today’s standards. However, built by the ancient civilizations these were designed to tell their users about the time of year based on the position of the moon, sun or stars. Stonehenge is perhaps the most wellknown example of stone circles. One theory suggests that they were aligned so that the sun would rise within a certain stone configuration only during the shortest day of the year. ASTROLABE An instrument that was developed in ancient times (Aristotle and Ptolemy’s time) and could be used to measure the height of a celestial body above the horizon. This lead to more accurate observations of the sky. TELESCOPES The earliest was used by Galileo and could only make an object seem 20x closer Newton invented the reflecting telescope which greatly improved the strength of magnification.