World History 9 Chapter 22 Section 1 “The Scientific Revolution
advertisement
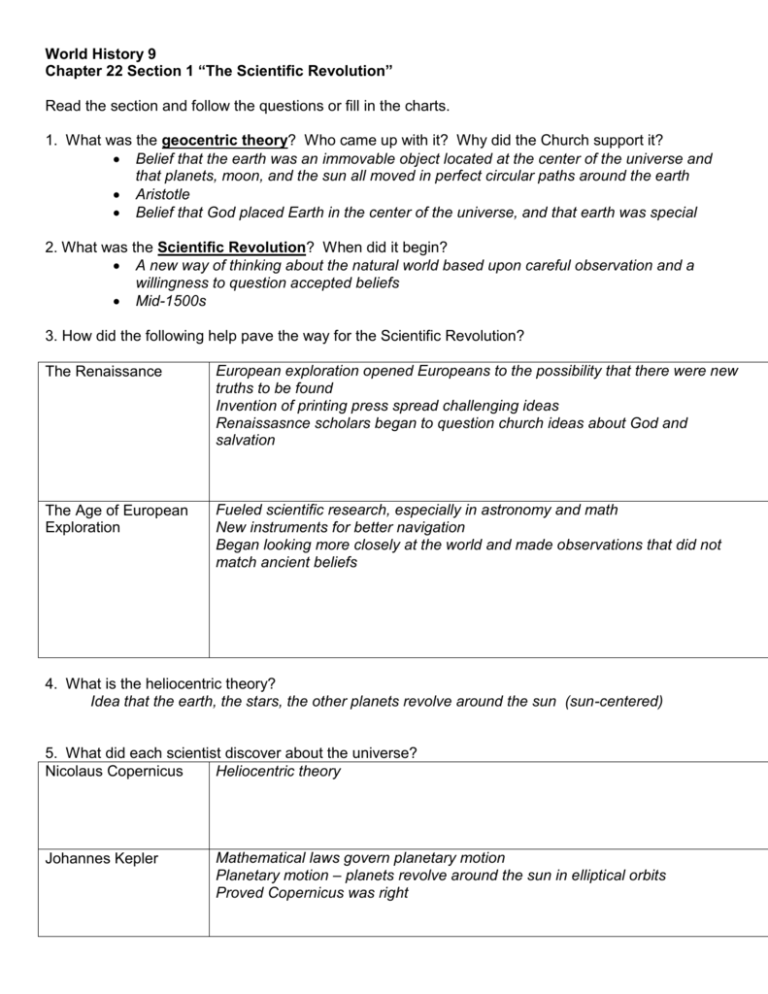
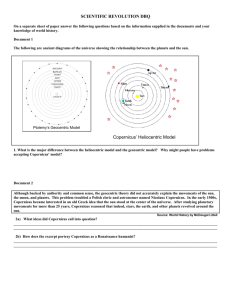
World History 9 Chapter 22 Section 1 “The Scientific Revolution” Read the section and follow the questions or fill in the charts. 1. What was the geocentric theory? Who came up with it? Why did the Church support it? Belief that the earth was an immovable object located at the center of the universe and that planets, moon, and the sun all moved in perfect circular paths around the earth Aristotle Belief that God placed Earth in the center of the universe, and that earth was special 2. What was the Scientific Revolution? When did it begin? A new way of thinking about the natural world based upon careful observation and a willingness to question accepted beliefs Mid-1500s 3. How did the following help pave the way for the Scientific Revolution? The Renaissance European exploration opened Europeans to the possibility that there were new truths to be found Invention of printing press spread challenging ideas Renaissasnce scholars began to question church ideas about God and salvation The Age of European Exploration Fueled scientific research, especially in astronomy and math New instruments for better navigation Began looking more closely at the world and made observations that did not match ancient beliefs 4. What is the heliocentric theory? Idea that the earth, the stars, the other planets revolve around the sun (sun-centered) 5. What did each scientist discover about the universe? Heliocentric theory Nicolaus Copernicus Johannes Kepler Mathematical laws govern planetary motion Planetary motion – planets revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits Proved Copernicus was right Galileo Galilei Studied the heavens Observed that Jupiter had 4 moons, the surface of the moon was uneven, and the sun had dark spots Disproved Aristotle’s theory that moon and stars were made of a pure, perfect substance Observations and laws of motion supported Copernicus Isaac Newton Same force rules motion of the planets and all matter on earth and in space Law of universal gravitation 6. How did Copernicus think the Church would react to his idea and why? They would reject it because it contradicted Church views 7. What happened to Galileo after the publication of his book Starry Messenger? Tried by the Inquisition. Forced to recant, saying Copernicus was wrong. 8. What is the scientific method? What are the steps? Logical procedure for gathering and testing ideas Problem or question – hypothesis – test with experiment – analyze and interpret data – draw a conclusion 9. What were the ideas of the following? Francis Bacon Idea of empiricism (experimental method) Believed by better understanding world, scientists could improve life Shouldn’t rely on conclusions of ancient thinkers Instead should experiment and draw conclusions René Descartes Scientists need to reject old assumptions and teachings Rely on math and logic Everything should be doubted until proved by reason Only think we know for certain is that we exist I think, therefore I am 10. What important developments took place in the following areas? Scientific instruments Development of microscope Anton van Leeuwenhoek used microscope to observe bacteria Mercury barometer for measuring barometric pressure and predicting weather Fahrenheit and Celcius created thermometers Medicine Andreas Vesalius dissected human corpses and published book with detailed drawings of organs, bones, muscle Edward Jenner introduced smallpox vaccine (used germs from cowpox) Chemistry Robert Boyle – use of scientific method in chemistry – founder of modern Chemistry; said matter is made up of smaller primary particles that joined together in different ways. Boyle’s Law – explains how volume, temperature, and pressure of gas affect each other 11. How did the ideas of reason and order affect ideas in politics? People began to rethink old ideas about the rights and liberties of ordinary citizens. Helped bring in ideas that challenged old relationship of government and people.