Photosynthesis
advertisement

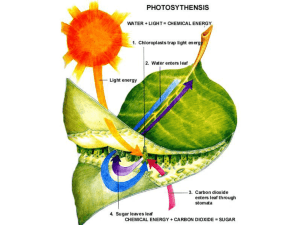
Where it starts:? Photosynthesis • Before photosynthesis evolved, – Earth’s atmosphere had little free oxygen • Oxygen released during photosynthesis changed the atmosphere Then – Favored evolution of new metabolic pathways, including aerobic respiration Now Sunlight as an energy source • Visible light – A small part of a spectrum of electromagnetic energy radiating from the sun • Electromagnetic energy – Travels in waves – Is organized as photons Photosynthetic Pigments • Photosynthesis begins when photons are absorbed by photosynthetic pigment molecules • Pigment molecules absorb only light of particular wavelengths – Photons not captured are reflected as color Major Photosynthetic Pigments • Chlorophyll a – Main photosynthetic pigment – Absorbs violet and red light (appears green) • Chlorophyll b, carotenoids, phycobilins – Absorb additional wavelengths • Collectively, photosynthetic pigments absorb almost all of wavelengths of visible light Overview of photosynthesis • Photosynthesis proceeds in two stages – Light-dependent reactions – Light-independent reactions 6H2O + 6CO2 6O2 + C6H12O6 Sites of photosynthesis: chloroplasts • Light-dependent reactions occur at a muchfolded thylakoid membrane – a single, continuous compartment inside the stroma (chloroplast’s semifluid interior) • Light-independent reactions occur in the stroma Products of light-dependent reactions • Typically, sunlight energy pass to photosystems (I, II) • pull electrons from water – release them – drives formation of ATP and NADPH • Oxygen is released from the chloroplast (and the cell) Light independent reactions: the sugar factory • Light-independent reactions proceed in the stroma • Carbon fixation: Enzyme rubisco attaches carbon from CO2 to RuBP to start the Calvin– Benson cycle Calvin–Benson Cycle • Cyclic pathway makes glucose – uses energy from ATP, hydrogen and electrons from NADPH – carbon and oxygen from CO2, • Reactions use glucose to form photosynthetic products (sucrose, starch, cellulose) Plant adaptations to environment • Environments differ – Plants have different details of sugar production in lightindependent reactions • On dry days, plants conserve water by closing their stomata – O2 from from photosynthesis cannot escape • Photorespiration reduces efficiency of sugar production Plant adaptations to environment • C4 plants – Carbon fixation occurs twice – First reactions release CO2 near rubisco, limit photorespiration when stomata are closed Plant adaptations to environment • CAM plants – Open stomata and fix carbon at night A burning concern • Photoautotrophs remove CO2 from atmosphere; metabolic activity of organisms puts it back • Human activities disrupt the carbon cycle – Add more CO2 to the atmosphere than photoautotrophs can remove • Imbalance contributes to global warming