Catalyst
advertisement

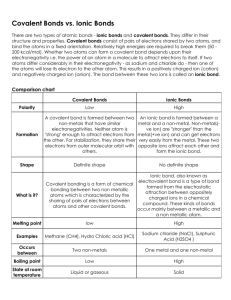
What is a covalent bond? Catalyst Atoms ___________ one or more electrons with each other to form the bond. Each atom is left with a ________________ outer shell. A covalent bond forms between two _________________. End Stick a Fork In It! Justify – TPS •Why don’t you put a fork in a power outlet? What property of the fork are you trying to avoid? LECTURE 2.4 – METALLIC BONDS WHAT ARE METALLIC BONDS? Today’s Learning Target •LT 2.5 – I can define a metallic bond and explain the role of electrons in the formation of these bonds. Chemical Bonding Ionic Bonds Metallic Bonds Covalent Bonds I. Metallic Bonds •This is a bond between multiple metal atoms •Only involves valence electrons •Forms between many metal atoms, so electrons are free to jump between atoms. •Therefore, valence electrons can be transferred with little to no work II. “Sea of Electrons” •This ability to roam creates a “sea of electrons” within a metallic bond •This means that heat and charge can be easily passed between multiple atoms in a metallic bond. •This is why metals are good conductors The core of the planet Jupiter could be said to be held together by a combination of metallic bonding and high pressure induced by gravity. HOW DO YOU IDENTIFY COMPOUNDS AS IONIC, COVALENT OR METALLIC? I. Identifying Compounds •If it is made of a metal and a non-metal, then it is an ionic •If it is made of only non-metals, then it is a covalent. •If it is made of only metals, then it is metallic. SUMMARIZE Identify that Compound! Practice Benchmark Quiz Thurs/Fri •You will have 40 minutes to complete the multiple choice benchmark •This should be done without notes and should be completed silently. Study to get ready! Closing Time • Study the different chemical bonds and their criteria! You’re gonna ace this test