Covalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds
advertisement

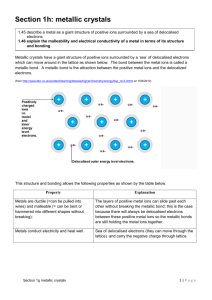
Covalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds There are two types of atomic bonds - ionic bonds and covalent bonds. They differ in their structure and properties. Covalent bonds consist of pairs of electrons shared by two atoms, and bind the atoms in a fixed orientation. Relatively high energies are required to break them (50 200 kcal/mol). Whether two atoms can form a covalent bond depends upon their electronegativity i.e. the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. If two atoms differ considerably in their electronegativity - as sodium and chloride do - then one of the atoms will lose its electron to the other atom. This results in a positively charged ion (cation) and negatively charged ion (anion). The bond between these two ions is called an ionic bond. Comparison chart Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds Polarity Low High Formation A covalent bond is formed between two non-metals that have similar electronegativities. Neither atom is "strong" enough to attract electrons from the other. For stabilization, they share their electrons from outer molecular orbit with others. An ionic bond is formed between a metal and a non-metal. Non-metals(ve ion) are "stronger" than the metal(+ve ion) and can get electrons very easily from the metal. These two opposite ions attract each other and form the ionic bond. Shape Definite shape No definite shape What is it? Ionic bond, also known as electrovalent bond is a type of bond Covalent bonding is a form of chemical formed from the electrostatic bonding between two non metallic attraction between oppositely atoms which is characterized by the charged ions in a chemical sharing of pairs of electrons between compound. These kinds of bonds atoms and other covalent bonds. occur mainly between a metallic and a non metallic atom. Melting point low High Examples Methane (CH4), Hydro Chloric acid (HCl) Sodium chloride (NaCl), Sulphuric Acid (H2SO4 ) Occurs between Two non-metals One metal and one non-metal Boiling point Low High State at room temperature Liquid or gaseous Solid Metallic bonding The particles in a metal are held together by metallic bonds. High melting and boiling points- Metallic bonds are strong and a lot of energy is needed to break them. This is why metals have high melting points and boiling points. Conducting electricity- Metals contain electrons that are free to move in the metal structure, carrying charge from place to place and allowing metals to conduct electricity well. Metallic bonding is the strong attraction between closely packed positive metal ions and a 'sea' of delocalized electrons. The attraction between the metal ions and the delocalised electrons must be overcome to melt or to boil a metal. Some of the attractions must be overcome to melt a metal and all of them must be overcome to boil it. These attractive forces are strong, so metals have high melting and boiling points. The delocalized electrons are able to move through the metal structure. When a potential difference is applied, they will move together, allowing an electric current to flow through the metal.