Brain - OCPS TeacherPress
advertisement

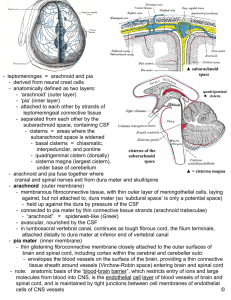
Brain Major partsWHAT of brain 2 THINGS DOES THE PONS CONNECT? 1. Brain stem – continuous with spinal cord; includes: 1. medulla oblongata- most inferior; a hard blow can be fatal; responsible for heart rate, breathing, reflexes: vomiting, coughing, swallowing, hiccupping, sneezing 2. Pons – superior to medulla; a “bridge” 3. Midbrain – reflex center for eyes/ears (tracking moving things/startle reflex), a “bridge” CAN YOU DESCRIBE THE NEURAL PATHWAY FOR “TRACKING”? 2. cerebellum: regulates posture and balance. 3. Diencephalon Includes: 1. thalamus – “bridge” 2. hypothalamus – inferior to thalamus; major regulator of homeostasis (monitor glucose levels, hunger/thirst, control of body temp, sleep patterns, drives/emotions) 3. epithalamus – contains pineal gland 4. cerebrum “seat of intelligence”; speech, memory, logical and emotional response, interpretation of sensation, voluntary movements Lobes: parietal, temporal, frontal, occipital Protection of the brain 1. Cranium 2. Meninges: dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater 3. Blood-brain barrier (BBB) – tight junctions of brain capillary cells preventing permeability of many substances (lipid soluble substances – O2, CO2, alcohols can cross) 4. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): shockabsorbing medium and allows exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and nervous tissue What are the parts of the diencephalon? a. Midbrain, thalamus, pons b. Thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus c. Midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata d. Cerebellum, midbrain, brainstem What are the parts of the brainstem? a. Medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain b. Diencephalon, pons, cerebellum c. Thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus d. Pineal body, pituitary gland, cerebral aqueduct What is the overall function of the brainstem? a. Processing/interpreting information b. Timing of skeletal muscles/coordination c. Producing CSF d. Controlling vital signs What is the order of meninges from CLOSEST to the brain to the skull (from deep to superficial)? a. Arachnoid mater, pia mater, dura mater b. Pia mater, arachnoid mater, dura mater c. Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater d. Pia mater, dura mater, arachnoid mater Cerebrum anatomy Cerebral hemispheres: right and left Cerebral cortex: outer rim of gray matter Gyri: folds of brain Fissures: deepest grooves (longitudinal fissure – separates right and left hemispheres) Sulci: shallower grooves Lobes of cerebrum frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital Separated by different sulci (ex: central sulcus separates frontal and parietal lobes) 2 main gyri: – precentral gyrus- anterior to central sulcus; part of frontal lobe; primary motor area (voluntary muscle contractions) – Postcentral gyrus – posterior to central sulcus; part of parietal lobe; primary somatosensory area (pain, touch, temperature, tickle, itch, etc)