General Characteristics
advertisement

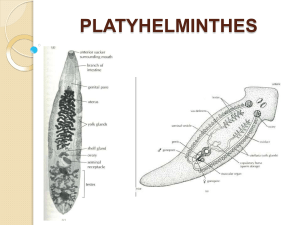
Platyhelminthes Kingdom: Animal Phylum: Platyhelminthes Class: Turbella Class: Trematoda Class: Cestoda Phylum Characteristics: General Characteristics aka. Flatworms Invertebrate Least complex worms 14,500 species Marine, freshwater, moist terrestrial environments Body Structure Bilateral symmetry Cephalization : have a clearly-defined anterior end, characteristic of motile animals, implies that the nervous tissue is concentrated at the anterior end Triploblastic : body wall consists of three cellular layers No body cavity , spaces between internal organs are filled (acoelomate) Digestion o Incomplete (mouth, but no anal opening) o 1st Pharynx: tube like, muscular organ, extends out of mouth, sucks in food o 2nd Gastrovascular cavity: food broken up by enzymes o 3rd Cells lining GC absorb nutrients through phagocytosis o 4th individual cells digest food o 5th some species (Planaria) have flame cells remove waste through pores on body surface by using cilia Nervous system Some species have a nerve net Most have very simple nervous system Planaria o Two nerve chords run down length of body, has sensory pits that detect chemicals and movement in water o Two sensors that detect light (eyespots) o Ganglion : located at head, receives messages from eyespots and sensory pits & can communicate with the rest of the body along the nerve chords Reproduction Asexually : Planaria - can re-grow body parts or an entire new body (regeneration) Sexual Life Cycle Sessile species usually parasites: obtain nutrients from inside host Platyhelminthes Classes Class: Tubellaria (Planarians) General Characteristics Free-living Mostly aquatic o o marine or freshwater, bottom dwellers (live in algae masses or under stones) few terrestrial live in humid forests Body Structure o Elongated, with triangular shaped head o Two anterior eye spots o Mouths in the middle of the ventral side Example: Dugesia tigrina (Planaria) Class: Trematoda (flukes) General Characteristics All are parasitic (mostly endoparasites) o Most hosts are vertebrate (sheep), but immature stages are often harbored in invertebrates (slug) Body Structure Oval and flattened Mouth at anterior end & may have adhesive suckers around the mouth Example: Fasciola hepatica ( Sheep liver fluke), Fasciola buski (Human liver fluke), Clonorchis sinensis (Chinese liver fluke) o o Class: Cestoda (tapeworms) General Characteristics All are endoparasites o o Adult worms live in the intestines of vertebrate hosts Larvae live in tissues of alternate hosts o Mostly slender and elongates with a flat body of many short segments (proglottids) Body Structure No mouth or digestive track; food is absorbed from host directly through body wall o Scolex : anterior segment, knob-like, covered in hooks o Stroblia : remainder of tapeworm, composed of proglottids (flattened segments) Example: Teania pisiformis (dog and cat tapeworms), Teania saginatum (sheep tape worm), Teania solium (human tape worm) o