Science 9 CFCs P. 238 Where was the first sight of the O
advertisement
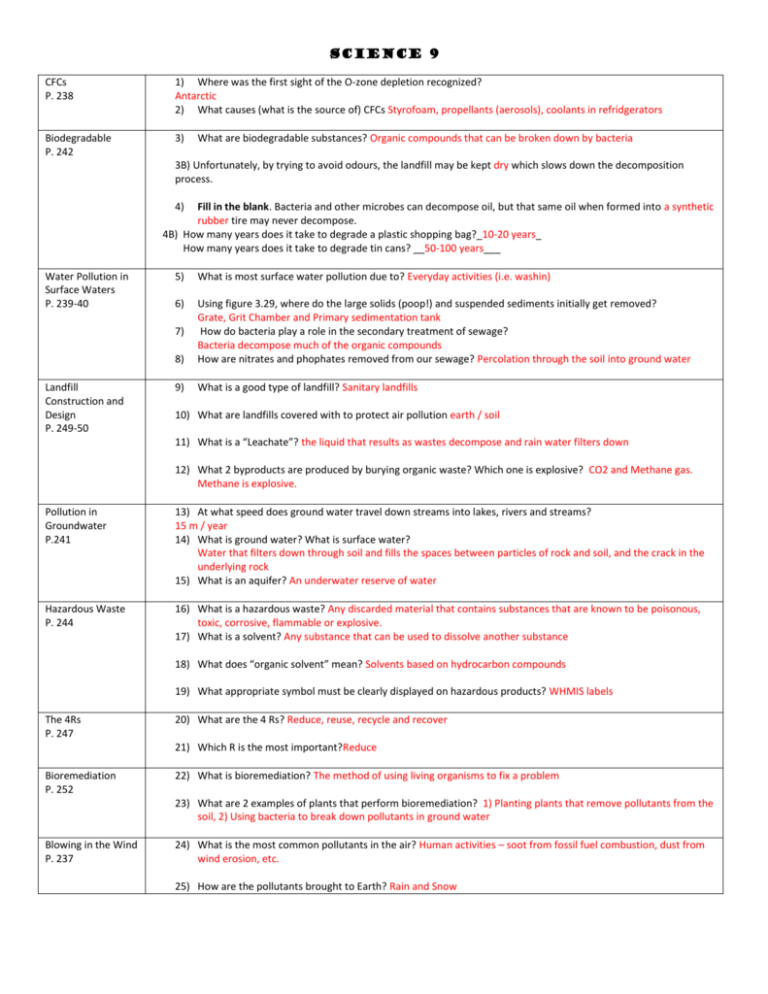
Science 9 CFCs P. 238 1) Where was the first sight of the O-zone depletion recognized? Antarctic 2) What causes (what is the source of) CFCs Styrofoam, propellants (aerosols), coolants in refridgerators Biodegradable P. 242 3) What are biodegradable substances? Organic compounds that can be broken down by bacteria 3B) Unfortunately, by trying to avoid odours, the landfill may be kept dry which slows down the decomposition process. 4) Fill in the blank. Bacteria and other microbes can decompose oil, but that same oil when formed into a synthetic rubber tire may never decompose. 4B) How many years does it take to degrade a plastic shopping bag?_10-20 years_ How many years does it take to degrade tin cans? __50-100 years___ Water Pollution in Surface Waters P. 239-40 5) What is most surface water pollution due to? Everyday activities (i.e. washin) 6) 8) Using figure 3.29, where do the large solids (poop!) and suspended sediments initially get removed? Grate, Grit Chamber and Primary sedimentation tank How do bacteria play a role in the secondary treatment of sewage? Bacteria decompose much of the organic compounds How are nitrates and phophates removed from our sewage? Percolation through the soil into ground water 9) What is a good type of landfill? Sanitary landfills 7) Landfill Construction and Design P. 249-50 10) What are landfills covered with to protect air pollution earth / soil 11) What is a “Leachate”? the liquid that results as wastes decompose and rain water filters down 12) What 2 byproducts are produced by burying organic waste? Which one is explosive? CO2 and Methane gas. Methane is explosive. Pollution in Groundwater P.241 13) At what speed does ground water travel down streams into lakes, rivers and streams? 15 m / year 14) What is ground water? What is surface water? Water that filters down through soil and fills the spaces between particles of rock and soil, and the crack in the underlying rock 15) What is an aquifer? An underwater reserve of water Hazardous Waste P. 244 16) What is a hazardous waste? Any discarded material that contains substances that are known to be poisonous, toxic, corrosive, flammable or explosive. 17) What is a solvent? Any substance that can be used to dissolve another substance 18) What does “organic solvent” mean? Solvents based on hydrocarbon compounds 19) What appropriate symbol must be clearly displayed on hazardous products? WHMIS labels The 4Rs P. 247 20) What are the 4 Rs? Reduce, reuse, recycle and recover 21) Which R is the most important?Reduce Bioremediation P. 252 22) What is bioremediation? The method of using living organisms to fix a problem 23) What are 2 examples of plants that perform bioremediation? 1) Planting plants that remove pollutants from the soil, 2) Using bacteria to break down pollutants in ground water Blowing in the Wind P. 237 24) What is the most common pollutants in the air? Human activities – soot from fossil fuel combustion, dust from wind erosion, etc. 25) How are the pollutants brought to Earth? Rain and Snow











