Chapter 18 outline
advertisement

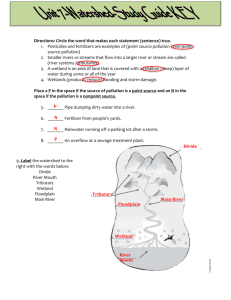
Chapter 18: Water Pollution Case Study and 18.1 Water Pollution 1. Identify and explain one ecological and economic benefit of creating an artificial wetland to act as a sewage treatment facility. 2. Explain how a constructed or natural wetland can treat wastewater. 3. Describe how a wetland can function as a sewage treatment plant. 4. List one goal of the Clean Water Act of 1972 5. Differentiate between point & non-point sources of water pollution. 18.2 Types and effects of water pollutants. 1. Name an infectious agent and its source. 2. Name the most serious water pollutant in terms of human health 3. Provide three examples of waterborne disease 4. Name the main source of pathogens that cause waterborne diseases 5. Explain why water is analyzed for coliform bacteria even if many are not pathogens. Oxygen Demanding Wastes 1. List three specific examples of oxygen demanding waste 2. Describe how the amount of DO in a lake can affect the type of fish in it. 3. Explain how BOD helps estimate the amount of organic waste in surface water 4. Describe how organic waste in a stream affects the BOD, DO and types of organisms before and after its point of input 5. Explain how human activities speeds up eutrophication 6. Explain how excessive nutrients create dead zones and contribute to red tides 7. Describe how dissolved oxygen levels can increase or decrease naturally in surface water. 8. Describe the water clarity and amount of plant growth in oligotrophic and eutrophic lakes Inorganic Pollutants: acids, bases metals, salts 1. Explain how mercury can get into an aquatic food chain (include the formation of methyl mercury) 2. Describe two ways that surface waters can become acidified. 3. Explain how the geology of an area can influence the acidification of surface water 4. What metal is leached into the environment due to increased acidity? Organic chemicals 1. Name the two sources of toxic organic chemicals for water contamination. 2. List two examples of organic pollutants, their source, and effect. 3. Name to chlorinated hydrocarbon pesticides that are toxic. 4. Explain why organic chemicals, such as birth control pills, should not be disposed of by flushing them down the toilet. Sediment 1. Describe how sediments can negatively affect the economy. 2. Describe how sediments can positively affect the environment. Thermal 1. Explain why changes in temperatures affect aquatic organism more than terrestrial ones. 2. Explain how a thermal plume is created and its effect on aquatic organisms SKIP READING all of 18.3 Water Quality Today Focus instead on 1. Know that the 1972 Clean Water Act a. has a goal of making all U.S. surfaces waters fishable and swimmable b. established a National Pollution Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) that requires industries or municipalities or any entity that discharges waste to surface water receive a permit. The permit requires disclosure of what is being dumped. c. In 1998 the EPA changed its management policy from the smaller river and navigable waterways management approach to a broader monitoring of watersheds. 2. List sources for the 12 leading causes( except impaired biota) of surface water impairment and explain how they affect water quality from figure 18.13. (p 406) 3. Explain what MTBE (methyl tertiary butyl ether) is and how it gets into groundwater. (p 408) 4. Identify an herbicide that can contaminate groundwater (p 408) 18.4 Water pollution control 1. Discuss examples of source reduction 2. Identify the types of pollutants associated with specific nonpoint sources and methods to control them a. Agriculture, Urban run-off, and Construction sites 3. Describe how a domestic septic tank works 4. Describe how Municipal Sewage Treatment Works a. Primary Treatment, Secondary Treatment, and Tertiary Treatment SKIP READING 18.5 Water Legislation 1. Safe Drinking Water Act: regulates water quality in commercial and municipal systems 2. Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA) 3. remediation of toxic waste sites Vocabulary Atrazine Bioaccumulation Biological oxygen demand Biomagnification CERCLA Cholera Clean Water Act of 1972 Coliform bacteria Cultural eutrophication Dead zones (hypoxic) Digesters Dissolved oxygen Dysentery Effluent Eutrophic Methyl mercury Non-point source Oligotrophic Oxygen sag Point source Primary treatment Red tide Safe Drinking Water Act: Thermal stratification