Respiratory System
advertisement

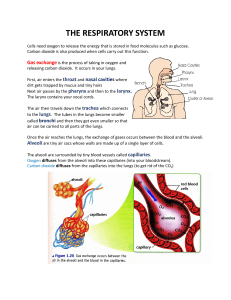
Respiratory System MUHAMMAD HAMMAD AP BIOLOGY BLOCK 6 Functions The main function of the respiratory system is gas exchange. When one inhales, oxygen enters the blood by means of alveoli and capillaries. It is then carried to different tissues by blood. Carbon dioxide is collected by the blood and carried to the lungs. CO2 diffuses from the capillaries and is exhaled as a waste product. Importance The human needs oxygen to sustain itself. Anoxia- complete lack of oxygen Hypoxia- decrease in oxygen ***After 4 to 6 minutes with anoxia or hypoxia, brain cells are completely destroyed leading to death. Organs of the Respiratory System Lungs- supply the body with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. They are present in the pleural cavities. Nose- organ through which air is inhaled and exhaled Pharynx- allows the passage of air to the lungs. Located behind the nasal and oral cavities. Epiglottis- prevents food or water from entering the trachea. Flap like structure. Larynx- controls the flow of air Trachea- facilitates the flow of air to the bronchi. Also known as the windpipe. Bronchi- passage which allows the flow of air to the lungs. Alveoli-interface for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between lungs and capillaries. Sac shaped bodies Diaphragm-creates a partition between the thoracic and abdominal cavity Quick Facts The rate at which human beings breathe is 12-18 breaths per minute. There are 1440 minutes in 24 hours, therefore, the average number of breaths drawn in by a human (at a rate of 12 breaths per minute) in a day's time is 17,280. There are over 600 million alveoli in the lungs of an adult human being. The right and left lungs of the human respiratory system do not have the same size. In fact, the left lung is a bit smaller than the right one.