File - singhscience
advertisement

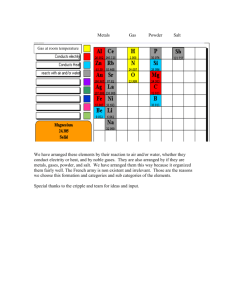
End of Chapter Test Revision PowerPoint Melting and Boiling Points The melting point is the temperature at which a solid to a .............. liquid substance changes from a ............ The boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid to a .............. gas substance changes from a ............ 0 and boils at 100 Water melts at .....°C ...... °C. Metals and non-metals in the periodic table The periodic table is a list of all the known elements that are arranged according to the similarities in their properties. Metals are on the left and in the centre. Non-metals are mostly on the right. What type of elements are between metals and non-metals? Some extra Information about the periodic table • As you go across the periodic table the number at the top of each element gets higher. • This is the relative atomic mass of the element. • The higher the relative atomic mass the bigger the element. What are the properties (features) of metals? • • • • • Good conductor of electricity Good Conductor of heat Shiny High Density (heavy for its size) Malleable (you can hammer into different shapes) What are the properties of nonmetals? • • • • • Poor conductors of electricity Poor conductors of heat Dull Low density Brittle Group 1 Metals Alkali Metals You need to know about there reactions with water (Equations must also be written in this format!) • Lithium + Water • Potassium + water • Sodium + Water Lithium Hydroxide + Hydrogen Potassium Hydroxide + Hydrogen Sodium Hydroxide + Hydrogen Lets look at some of the alkaline metals we can’t use in school! • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m55kgyA pYrY Features of Group 1 Metals • Like all metals they are good conductors of electricity and heat. • Shiny when cut • They get more reactive as you go down a group. • There boiling point goes down as you go down the group. Group 7 Elements The Halogens Properties of Halogens Need to learn! Element Symbol State at Colour room temperature Fluorine F Gas Pale Yellow Chlorine Cl Gas Yellow-Green Bromine Br Liquid Red-Brown Iodine I Solid Grey Group 7 Reactions with Iron • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EvtyMr5E vBY What happens to the reactivity of group 7 metals as we go down the group? Displacement Reactions • Step 1- Order the elements into reactivity. The most reactive at the top and the least reactive at the bottom. Chlorine Bromine Iodine Chlorine Most Reactive Bromine Iodine Least Reactive Displacement Reactions • The more reactive element always beats (displaces) the less reactive element. e.g. Chlorine + Potassium Bromide Potassium Chloride + Bromine Your Turn • Bromine + Potassium Iodide • Chloride + Sodium Bromide • Iodine + Potassium Chloride Group 0 Elements Noble Gases Features of Group 0 • The Group 0 elements are known as the noble gases. They are un-reactive, which means they do not react easily. They show some patterns in their chemical and physical properties. For example, the elements lower down the group are slightly more reactive than those at the top of the group. Why are they called the ‘noble gases’? The noble gases all form colourless gases at room temperature. They are all very unreactive. Noble gases were originally called ‘inert gases’, as they were thought not to react with anything. Then in 1962, a British chemist, Neil Bartlett, made a compound with xenon. The name was changed to ‘noble gases’ as they were considered similar to the very unreactive precious metals gold and platinum, which are sometimes called ‘noble’ metals. Now only neon and helium have not yet been made to form compounds.