Chemistry Name: Ms. Boon Period: ______ Date: ______ Unit 2
advertisement

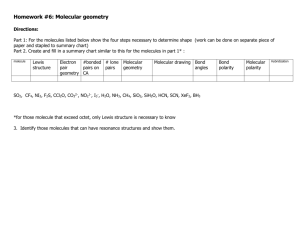
Chemistry Ms. Boon Name: ___________________ Period: _______ Date: __________ Unit 2 Chemical Bonds Day 5: Building Models of Molecules Lab Introduction: The shape of a molecule greatly affects its properties including whether it is polar or nonpolar. In this activity you will use modeling materials to determine the shapes of several small molecules. To determine the correct shape, you must keep track of both bonding and lone (unshared) pairs of electrons. You will draw Lewis structures of molecules and practice naming the geometrical shapes of molecules. Pre-laboratory Notes In a covalent bond, atoms _______________ electrons. Nonpolar covalent bond = electrons are _______________________. Why? Atoms have similar electronegativities, so they pull on the electrons equally. Polar covalent bond = electrons are _______________________________. Why? Atoms have different electronegativities, so they pull on the electrons unequally. A covalent bond in which two atoms share one pair of electrons is called a _________ bond. A covalent bond in which two atoms share two pairs of electrons is called a _________ bond. A covalent bond in which two atoms share three pairs of electrons is called a ___________ bond. Why? Atoms share as many electrons as necessary to meet the octet rule. Pictures/Examples: Materials molecular model kit or assorted toothpicks and marshmallows glossary of molecular shapes and names Procedure 1. To plan your models, Draw Lewis Dot Diagrams for each molecule listed in Data Table 1. 2. Before beginning to build, check your Lewis Dot Diagrams with the answer key or get teacher approval. 3. Use the provided modeling materials to build the molecules listed in Data Table 1. If using toothpicks, use a colored toothpick for lone pairs and plain toothpicks for bonds. 4. Position the atoms and lone pairs of electrons as far apart from each other as possible. 5. Match your model to the closest molecular shape shown in the glossary of molecular shapes. 6. List the name of the shape in Data Table 1. 7. Examine the shape of each molecule. Based on the shape, is the molecule polar or nonpolar? Record your answer in Data Table 1. 8. Cleaning up: Take apart your models. Return all materials as instructed by your teacher. Data Table 1 Carbon dioxide: CO2 Water: H2O Molecular Shape: Polarity: Molecular Shape: Polarity: Formaldehyde: H2CO Hydrogen Cyanide: HCN Molecular Shape: Polarity: Difluoromethane: CH2F2 Molecular Shape: Polarity: Molecular Shape: Polarity: Molecular Shape: Polarity: Sulfur dioxide: SO2 Molecular Shape: Polarity: Phosphorous Trichloride: PCl3 Molecular Shape: Polarity: Nitrogen gas: N2 Ozone: O3 Molecular Shape: Polarity: Chemistry Ms. Boon Name: ___________________ Period: _______ Date: __________ Post Laboratory Analysis Questions (Answer on a separate sheet of paper. Use complete sentences.) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Compare your models to the Lewis Dot Diagrams that you drew in the data table. How are the similar? How are they different? Which molecules contained at least one double bond? How did you know? Which molecules contained at least one triple bond? How did you know? Which molecules contained all single bonds? How did you know? Group together molecules that have the same number of atoms coming off the central atom. Do these molecules have the same molecular shape? In the models, why are atoms and lone pairs of electrons positioned as far apart as possible? If you only look at the chemical formula of a molecule, can you determine its shape? Why or why not? By looking at the geometry of a molecule, how can you determine if it is polar or nonpolar? Glossary of Molecular Shapes More Practice Drawing Molecules. Draw the Lewis Dot Structures for the molecules and polyatomic ions listed below.c sulfur dichloride, SCl2 arsenic trifluoride, AsF3 silicon tetrahydride, SiH4 trifluoromethane, CHF3 acetate, CH3COO- ammonium NH4+ Nitrate, NO3- Hydroxide, OH- Hydronium, H3O+