Lymphatic System
advertisement

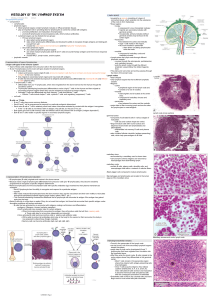
Lymphatic System Chapter 20 An Overview • One way system flowing towards heart • Functions – Return fluid and proteins to venous blood – House phagocytic cells and lymphocytes – Carry absorbed fats from intestines to blood • Components – Lymphatic vessels – Lymph – Lymph nodes Lymphatic Vessels • Capillaries – Endothelial cells form minivalves – Inflammation increases permeability – Lacteals carry fat from intestines as chyle • Collecting Vessels – Similar to veins – Varies between individuals • Trunks – – – – – Lumbar Bronchomediastinal Subclavian Jugular Intestinal • Ducts – Right lymphatic – Thoracic • Cisterna chyli • Dump to venous blood Lymph Transport • Low pressure system w/o a pump – Similar return as veins – Arterial pulsations – Tunica media smooth muscle contraction • Balances with blood fluid loss – Hydrostatic and colloid pressures (Chpt. 19) – ~ 3L every 24 hours • Rate increases w/activity Lymphocytes • Primary fighters of immune response • Targets are antigens • T-cells – direct attack – Attack and destroy antigens • B-cells – indirect attack – Produce antibodies from plasma cells to ‘flag’ antigens Other Lymphoid Cells • Macrophages – Phagocytic themselves – Activate T-cells • Dendritic cells – Capture and move antigens to lymph nodes – Activate T-cells too • Reticular cells – Fibroblast-like cells that form supportive network Lymphoid Tissue • Proliferation & surveillance sites • Primarily reticular CT (except thymus) – Diffuse lymphatic tissue • Sparse scatterings in all lymph organs, • Concentrated in lamina propria of mucus membranes – Lymphoid follicles (nodules) • Spherically packed tissue w/o capsule – Larger organs and few isolated patches • Germinal centers where B cells proliferate – Enlarge w/ increased B cell division Lymph Nodes • Main lymphatic organs • Located along lymph vessel path – Concentrated near large collecting vessel junctions • Inguinal region • Axillary region • Cervical region • Functions – Filtration • Macrophages prevent foreign molecule entrance to blood – Immune system activation • Monitor for antigens to fight Lymph Node Structure • Dense fibrous capsular outside – Difference b/w node and nodule – Invaginates forming trabeculae • Regions – Medulla • Macrophages, T cells, B cells, and plasma cells • Lymph sinuses: capillaries where macrophages ‘hunt’ – Leaking antigens activate lymphocytes in tissue – Cortex • Dense nodules w/germinal centers • Transient T cells Lymphatic Circulation • Enters node in afferent lymphatic vessels • Large subscapular sinus to smaller, cortical sinuses • Enter medulla • Exit at hilum via efferent lymphatic vessels – Fewer slows flow – Allows lymphocytes & macrophages to work Spleen • Largest lymphatic organ • Functions – Lymphocyte proliferation and surveillance – Stores products of RBC breakdown and platelets – Cleanse blood • Remove aged/damaged blood, debris, and foreign matter • Fetal erythrocyte production (ceases after birth) • Distinct areas – White pulp w/lymphocytes act in immune functions – Red pulp w/worn out erythrocytes and pathogens Thymus • Bilobed organ at base of neck – More pronounced when young – Corresponds w/importance of immune function • T lymphocyte maturation only – Lacks B cells – Doesn’t directly fight antigens • Thymocytes secrete thymosin and thymopoietin to signal T cell maturation Tonsils • Lymphatic tissue ring around pharynx – – – – Palatine: largest and most likely infected Lingual Pharyngeal (adenoids) Tubal • Follicles w/germinal centers • Gather and remove pathogens from pharynx – Crypts are deep invaginations to trap and destroy • Tonsil stones – Produces ‘memory’ immune cells for future attacks Mucosa-Associated Lymphatic Tissue (MALT) • Collections of lymphatic tissue to protect external environment openings • Peyer’s patches – In walls of small intestine – Destroy bacteria before it leaves intestines – Generate ‘memory’ lymphocytes • Appendix – Junction of small and large intestine – Similar function as Peyer’s patches • Lymphoid nodules – In walls of bronchi Homeostatic Imbalances • Tonsillitis: inflammation of tonsils • Lymphangitis: vasa vasorum of lymph vessels congested w/blood • Lymphedema: blockage prevents return to blood • Buboes: inflamed lymph nodes • Splenectomy: removal of a ruptured spleen • Appendectomy: removal of appendix • Elephantiasis: lymph vessels clogged by worms causing increased swelling • Hodgkin’s disease: malignant B-cells • Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: any lymphoma, but Hodgkin’s