Unit 10: Lymphatic System
advertisement
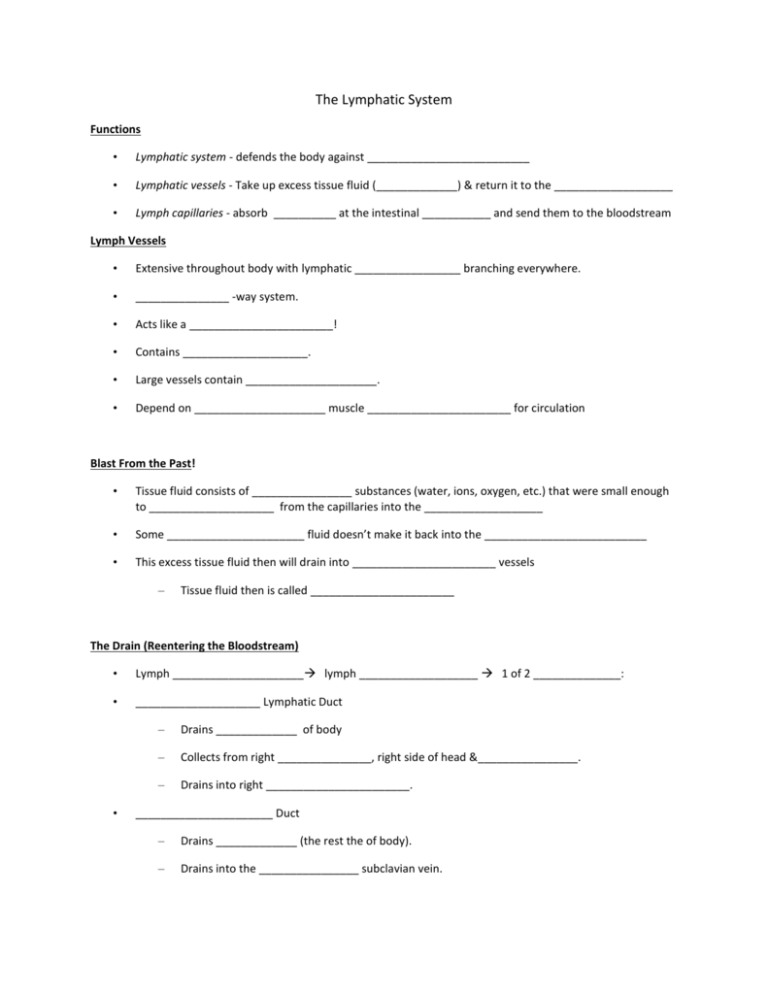
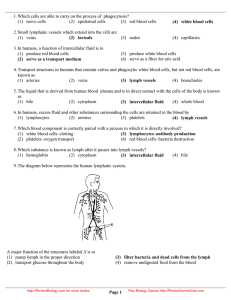
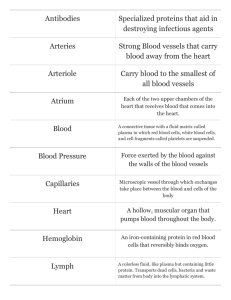
The Lymphatic System Functions • Lymphatic system - defends the body against __________________________ • Lymphatic vessels - Take up excess tissue fluid (_____________) & return it to the ___________________ • Lymph capillaries - absorb __________ at the intestinal ___________ and send them to the bloodstream Lymph Vessels • Extensive throughout body with lymphatic _________________ branching everywhere. • _______________ -way system. • Acts like a _______________________! • Contains ____________________. • Large vessels contain _____________________. • Depend on _____________________ muscle _______________________ for circulation Blast From the Past! • Tissue fluid consists of ________________ substances (water, ions, oxygen, etc.) that were small enough to ____________________ from the capillaries into the ___________________ • Some ______________________ fluid doesn’t make it back into the __________________________ • This excess tissue fluid then will drain into _______________________ vessels – Tissue fluid then is called _______________________ The Drain (Reentering the Bloodstream) • Lymph _____________________ lymph ___________________ 1 of 2 ______________: • ____________________ Lymphatic Duct • – Drains _____________ of body – Collects from right _______________, right side of head &________________. – Drains into right _______________________. ______________________ Duct – Drains _____________ (the rest the of body). – Drains into the ________________ subclavian vein. Lymph Organs • Organs that contain _____________________________ - Type of ____________________ - 2 types: __________ & __________ • Lymph__________________: - ________________________ - ________________________ - ________________________ - ______________________________________ Spleen • Located in ________________ left abdomen below ___________________________. • Divided into _________________ containing _____________________. • Sinuses filled with ____________________. • Acts as a ____________________________ for blood. • ____________________ blood as it passes through. • ____ cells produce ______________________ in spleen. Lymph Nodes • Small round ___________________ that occur along lymph vessels. • Contain __________________________ • ___________________ (empty sacs) inside nodules filled with ___________________________. • Purifies ____________________ as it passes through. • Kills _________________ organisms. • Located in large numbers at certain points in body. - Examples: Tonsils • Partly _________________________ lymph nodules • 3 kinds: – _____________________________ - (adenoids) back of nasal passage. – _____________________________ - base of tongue most commonly removed. – _____________________________ - 2 large organs on sides of uvula rarely removed. Thymus • Located resting on the ____________________, superior to the ______________________. • Larger in _______________________. • Matures ____ lymphocyte cells. • Produces the hormone ____________________ which causes pre-T cells to ______________ into T cells. • Adds _______________________ to infants. Thymus Anatomy • ____________________ - divisions where lymphocytes are produced. • ____________________ - outer part of lobule, less mature T cells are located here. • ____________________ - inner part of lobule, more mature T cells are located here. 2 Kinds of Defenses • • ____________________________ – Barriers to _____________________ : skin & mucus membranes – Inflammatory Reaction: release of ____________________ & wbc’s to phagocytize (eat) bacteria – Protective ____________________: complement systems (plasma protein chain reaction) kicks in to attack__________________________. – Example: __________________________ binds to viruses receptors cells. _____________________________ – B (___________ marrow) lymphocytes: mature in the bone & become plasma cells that produce ________________________. – T (____________) lymphocytes: mature in the thymus & directly attach to cells bearing antigens. Immunity • • _______________________ MEDIATED – _____ cells are responsible – Foreign bodies stimulate the _______________ B cell to divide many times (____________) – Some B cells produce specific ___________________ that target _________________ & destroy. – Some _______________ B cells are also produced to maintain immunity. _____________________ MEDIATED – _____ cells are responsible – T cells then directly _________________ this complex. – __________________ T cells finally stimulate B cells to release_______________________. Antibodies – Antibodies are proteins produced in the presence of some foreign substance in the blood – Produced by B cells that become plasma cells. – Antigens are foreign invaders (usually a protein) that stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies. – Antibodies are very specific for antigens. Immunotherapy • Ability to defend against infectious organisms, foreign cells, & cancer cells. • Primarily the result of B cells & T cells. • Active immunity occurs after an infection from a bacteria or virus. Long lasting immunity. • Vaccinations stimulate active immunity by introducing weak or dead pathogen. • Passive immunity occurs when an antibody is given to a person to fight an infection. Short lasting. • Lymphokines are immune stimulating proteins released by T cells.