Back to A+P II
advertisement

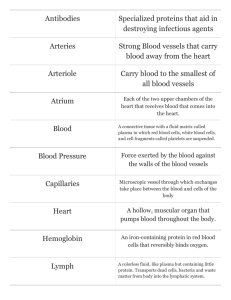
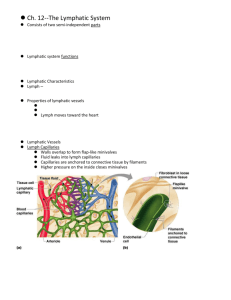
Lab 7 The Lymphatic System and Immune Response - Exercise 35A Report on Blood Typing from Lab 6 Lecture in Lab - Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic System and Immune Response Activity 1: Identifying the Organs of the Lymphatic System Activity 2: Studying the Microscopic Anatomy of a Lymph Node…, 1. Use the ileum with Peyer's Patches slide and identify Peyer's Patches. Use Plate 35 as a reference. Activity 3: Using the Ouchterlony Test to Identify Antigens, 1 - 8 Name____________________________ Lab Section ________________ Review Sheet A B C D E F 1. Match the labels on the figure with the terms below. ___ Axillary nodes ___ Inguinal nodes ___ Cervical nodes ___ Right lymphatic ___ Cisterna chyli duct ___ Thoracic duct A B C D 2. Match the labels on the figure with the terms below. ___ Peyer's patches ___ Spleen ___ Thymus ___ Tonsils 3. What is the source of lymph in the lymphatic system? 4. How is lymph propelled through the lymphatic vessels? 5. Name two places where lymph is returned to the circulatory system. a. ____________________________________ b. ____________________________________ 6. Describe two ways that lymph vessels are structurally similar to veins. a. b. 7. Why is lymph often cloudy or milky looking in the cisterna chyli? ________________________________________________________________________ C A D E B F 8. Match the labels on the figure with the terms below. ___ Afferent vessels ___ Capsule ___ Cortex ___ Efferent vessels ___ Germinal center ___ Medullary cords and sinuses 9. Why are there fewer efferent than afferent vessels? 10. If you are looking for the following immune system cells in a lymph node, where would you look? B cell ____________________________ T cell ____________________________ Macrophage ____________________________ 11. Match the following structures with the correct function. ___ B cells ___ Lymph node ___ Macrophage ___ Spleen ___ Thymus A. T cells develop self-tolerance and immunocompetence here B. Major site for presentation of antigens to B and T cells C. Removes damaged red blood cells and other debris from circulation D. Produce clones of antibody- producing plasma cells E. Large phagocyte which also acts as an antigen presenting cell Ouchterlony Double-Gel Diffusion Results 1. Demonstration of diffusion using dye. Draw the appearance of section I in your dish after 30 to 45 minutes. Use red and green colored pencils. 2. Draw section II as it appears after incubation for 16 to 48 hours. Be sure to number the wells. 3. Draw section III as it appears after incubation for 16 to 48 hours. Be sure to number the wells. Unknown # ____________ 4. What evidence for diffusion did you observe in section I? 5. Is there any evidence of a precipitate in section I? ____________________________ 6. Which of the sera functioned as the antigen in section II? _______________________ 7. a. Which antibody reacted with the antigen in section II? _______________________ b. How do you know? Be specific about your observations. 8. If swine albumin were placed in well 1 in section II, what would you expect to happen, and why? 9. If chicken albumin were placed in well 1 in section II, what would you expect to happen, and why? 10. a. What antigen(s) was (were) present in the unknown solution? b. How did you know? (Be specific about your observations.) 11. In what way is the Ouchterlony technique similar to the technique you used for blood typing in an earlier lab?