Honors Biology Chapter 10
advertisement

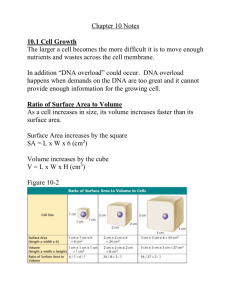
Section 1 To get bigger or make more cells that is the question? Limit to cell growth o DNA overload DNA’s function Protein synthesis, everything is made of proteins o Transport of materials As cell gets larger, what would happen to rate of diffusion of materials? Consider a plant cell Cell Size Surface Area (length x width x 6) Volume (length x width x height) Ratio of Surface Area to Volume To get bigger or make more cells that is the question? Limit to cell growth o DNA overload DNA’s function Protein synthesis, everything is made of proteins o Transport of materials As cell gets larger, what would happen to rate of diffusion of materials? Consider a plant cell Surface area L X W X # of sides Volume L X W X H Ratio Process of creating two new daughter cells from one o Genetically identical Purpose o Regulates the size of a cell o Repair of damaged cells o Replace old cells o Asexual Reproduction Section 2 Prokaryotes Cell division is a two step process o Copy DNA o Divide cytoplasm Eukaryotes Much more complex o Cell division includes two main processes Mitosis Cytokinesis Become visible in the cell only prior to cell division DNA becomes tightly coiled Structure Become visible in the cell only prior to cell division DNA becomes tightly coiled Structure Chromosome number G1 phase M phase S phase G2 phase Interphase o Preparation for mitosis o Normal cell activities o 3 sub phases G1 Phase(first gap) Cell growth Raw materials created for DNA synthesis S Phase (synthesis) DNA is replicated G2 Phase New organelles are created Proteins needed for spindle fibers are created M phase o Composed of two parts o Mitosis o Cytokinesis 4 phases Prophase o Chromosomes condense and become visible o Spindle fibers are created Centriole From microtubules o Nuclear envelope breaks down o Spindle fibers attach to chromatids within centromere 4 phases Prophase o Chromosomes condense and become visible o Spindle fibers are created Centriole From microtubules o Nuclear envelope breaks down o Spindle fibers attach to chromatids within centromere Metaphase o Chromosomes line up across middle 4 phases continued Anaphase o Centromeres break down o Sister chromatids separate Daughter chromosomes o Pulled by spindle fibers o At end, chromosomes are at opposite poles 4 phases continued Anaphase o Centromeres break down o Sister chromatids separate Daughter chromosomes o Pulled by spindle fibers o At end, chromosomes are at opposite poles Telophase o Chromosomes begin to uncoil o Spindle fibers break down o Nuclei reform Animal cell o Cytoplasm is pinched inward by proteins Actin and myosin Animal cell o Cytoplasm is pinched inward by proteins Actin and myosin Plant cells o Create a cell plate o Vacuoles are created by golgi apparatus Section 3 Cyclins o Protein family that when produced regulate passage of cell through cell cycle Two major types of regulation o Internal Checkpoints G1, G2, and M Stop signals o External Growth factors Proteins produced by cells that cause other cells to divide Ex. MPF (maturation promoting factor) Wound healing Speeds up process of cell division Density dependent Slows down Uncontrolled cell growth Divide to form masses of cells called tumors Uncontrolled cell growth Divide to form masses of cells called tumors o Benign o Malignant Uncontrolled cell growth Divide to form masses of cells called tumors o Benign o Malignant Environmental triggers o Carcinogens Genetic influence o p53 gene- oncogene o Normally does not allow cell to divide until it has the proper number of chromosomes