Cell Cycle and Mitosis
advertisement

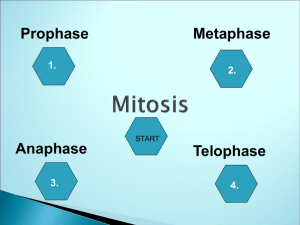
Warm-up 12/11: • Define the term Homologous? • What is a Haploid? Diploid? • Your somatic cells have 46 Chromosomes and are diploid cells, – How many chromosomes are in your haploid Gametes? • What do you call a photograph of all the chromosomes? Cell Cycle and Mitosis Cell Cycle • 3 major phases • Interphase: time between cell divisions - G phases: growth - S phase: copying of DNA • M phase (mitosis): division of the nucleus • Cytokinesis: division of the cytoplasm Mitosis (M phase) • • • • 2n 4n chromatids 2 (2n) Continuous process starts with interphase Need to separate the doubled chromosomes Four phases prophase metaphase anaphase telophase • PMAT Prophase • • • • • Can see chromosomes Chromatids stay connected by centromeres Nucleolus and nuclear membrane break down Centrosomes and centrioles appear Early mitotic spindle forms Metaphase • Two types of fibers (mitotic spindle) kinetechore fibers: attach to centromere of chromosome polar fibers: extend centrosome to centrosome, push cell apart • Fibers line up the chromosomes in middle Anaphase • Chromatids of each chromosomes are pulled apart by fibers • Move towards opposite poles of dividing cells Telophase • • • • • Chromosomes in opposite ends Spindle fibers break down Nuclear envelope reforms Nucleolus in each cell Cytokinesis MOVIE Homework • Chromosome Structure Due Monday • Observing Mitosis Due Tuesday • PQRST 154-159 Due Wednesday