Stem Cells
advertisement
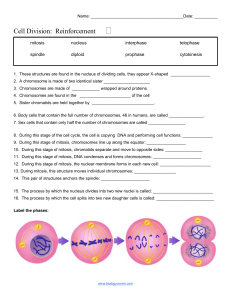
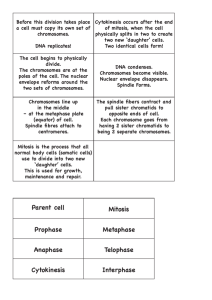
Why Would a Cell Divide? As cells absorb nutrients and get larger, the volume of the cell increases faster than the surface area Surface area for exchange not great enough to support cell’s needs This means that a cell can no longer absorb nutrients and get rid of wastes fast enough to support its demands (volume) So what’s a cell to do? Solution: divide in 2! Different cells divide at different rates: Most mammalian cells = 12-24 hours Some bacterial cells = 20-30 minutes Cell Type Typical Lifespan Intestinal Lining ? Skin Cell ? Red Blood Cell ? Liver Cell ? Intestine –Muscle ? and other tissue Cell Type Typical Lifespan Intestinal Lining 4-5 Days Skin Cell 2 Weeks Red Blood Cell 4 Months Liver Cell 300 – 500 Days Intestine –Muscle 16 years and other tissue Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis IPMATC • • • Chromosomes are copied (# doubles) Cell growth and organelles are doubled Preparing for mitosis Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) • Centrioles appear and begin to move to opposite end of the cell. • Spindle fibers form between the poles. • • Chromatids (or pairs of chromosomes) attach to the spindle fibers and line in middle. • Chromatids (or pairs of chromosomes) separate and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell. • • • Two new nuclei form. Chromosomes appear as chromatin (threads rather than rods). Mitosis ends. • Cell membrane moves inward to create two daughter cells – each with its own nucleus with identical chromosomes. Internal- Protein that regulates the timing of the cell cycle inside the cell (ex: cyclin). External- Protein that can cause the cell cycle to speed up or slow down (ex: growth factors, contact inhibition). *Apoptosis*-programmed cell death. Cancer – body loses ability to control growth. › *Damaged P53 gene* › Causes: tobacco, radiation exposure, viral infection, etc. Tumors- mass of cells › Can damage surrounding area › Can break off and spread throughout body Unspecialized cells process by which cells become specialized is known as differentiation. Replacing damaged heart cells.