Chemical Equations, Word Equations and Balancing
advertisement

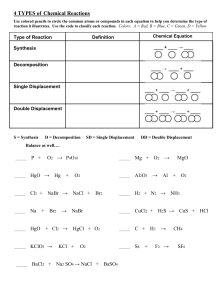
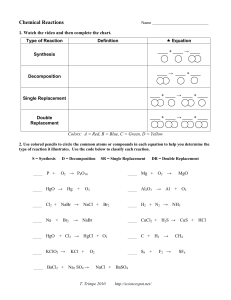
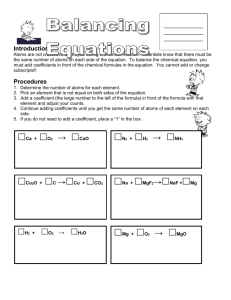
Chemical Equations, Word Equations and Balancing • THE MEANING OF A CHEMICAL EQUATION • A chemical equation is a chemist’s shorthand expression for describing a chemical change. As an example, consider what takes place when iron rusts. Example • Fe + O2 → Fe2O3 • In this expression, the symbols and formulas of the reacting substances, called the reactants, are written on the left side of the arrow and the products of the reaction are written on the right side. The arrow is read as “gives”, “yields”, or “forms” and the plus (+) sign is read as “and”. When the plus (+) sign appears between the formulas for two reactants, it can be read as reacts with. (The + sign does not imply mathematical addition). The equation, above, can be read as iron reacts with oxygen to yield (or form) iron(III) oxide. Word Equation • The same set up but the full name instead of chemical formula • • • • Fe + O2 → Fe2O3 SO it would be: Iron (s) + Oxygen (g) → iron(III)oxide (s) The word equation often includes the state of matter (s)(l)(g)(aq)-aqueous solution Law of Conservation of Mass • The mass of the reactants equals the mass of the products. • Sodium and oxygen react to create sodium oxide • Na + O2 Na2O (THIS DOES NOT HAVE THE SAME MASS) • Balanced: – – – – 4 Na + O2 2 Na2O 4 Na - 4 Na 2O -2O NOW IT IS BALANCED Balancing • From the word equation write a skeleton equation (unbalanced) • Then count the number of atoms of each element and match the number on the reactant side with the number on the product side. Examples • • • • • • Balance these equations: ___Cl2 + __ NaBr __ NaCl + __Br2 __ Ag2O __ Ag + ___O2 __Mg + ___ HCl __H2 + __MgCl2 ___ H2 + __O2 __ H2O __Cl2 + __ NaBr __ NaCl + __Br2 Answers • • • • • Cl2 + 2 NaBr 2 NaCl + Br2 2 Ag2O 4 Ag + O2 Mg + 2 HCl H2 + MgCl2 2 H 2 + O 2 2 H 2O Cl2 + 2 NaBr 2 NaCl + Br2