Male and Female Reproductive Systems.
advertisement

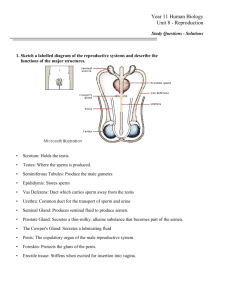
Male and Female Reproductive Systems. By Sammy Newbold. FHS 2400 The Reproductive system unit objectives • Be able to identify and define components of the male and female reproductive systems. • Understand disorders and disease of the reproductive systems. Discussion questions before the unit lesson • What are the reproductive systems functions? • What are Gonads and gametes? • Creation of offspring • Produces hormones • Metabolic and physiological process. Gonads are the organs that produce the sex cells or gametes. For men it is the Testes and for woman it is the ovaries. Gametes or also know as the sex cells, are produced in the gonads. The gametes for men is sperm and the egg for woman. • • • • • • • Penis Testes Epididymis Ductus deferens Seminal vesicles Ejaculatory duct Prostate gland • Urethra • Bulbourethral gland • scrotum Functions and Components of the Penis • The function of the penis is to conduct urine outside the body and to introduce sperm into the vagina • The penis is the largest organ in the male reproductive system. • The penis surrounds the urethra and consist of three different parts. – Body – Glans penis – Root of penis The body • The body of the penis is composed of three different masses of tissue. Each are bonded together by fibrous tissue. – The Corpus Cavernosum penis is the two most dorsal and lateral masses of the penis. – The Corpus Spongiosum penis is the smaller, mid ventral mass of the penis, which the urethra passes through. The root of the penis • Portion of the penis attached to the pelvic area Glans penis • Is located at the distal end of corpus Spongiosum, separated by a marginal area call the corona. It is covered by the loose skin called fore skin • Testis – Function is to produce sperm in the seminiferous tubes and produce male hormone testosterone. • Epididymis – Sight of sperm maturation – Almond shaped, lies posterior to testis and consist of tightly packed ducts called seminiferous tubules • Ductus deferens or vas deferens – Passage for sperm from epididymis to urethra – Long duct that connects the epididymis to ejaculatory duct • Seminal vesicles – Tubular glands found posterior of bladder. – Unites with vas deference to form ejaculatory duct. – Produce alkaline fluid and is 60% of semen • Ejaculatory duct – Posterior to bladder – Ejects sperm into prostatic urethra • Prostate gland – Inferior to bladder and surrounded by urethra – Secrets fluid rich in citric acid, prostatic acid, phosphate. – Is 30% of semen • Urethra – Located at base of bladder and goes through the penis. – Serves as passage way of urine and spermatozoa • Bulbourethral or Cowper’s gland – Inferior to prostate gland. – Secrets alkaline substance to neutralize acids in vagina and urethra. – First fluid released during sexual stimulation • Scrotum – Sac that holds testis – composed of skin, superficial fascia and skeletal muscle. Semen or seminal fluid • Mixture of sperm, and secretions from prostate gland and Cowper's gland. • Average volume is 2.5-5 mm of fluid • 50-150 million sperm per mm of semen The male hormone testosterone functions • • • • • • • • Controls growth and development Maintenance of the sex organs Stimulate bone growth Stimulate protein anabolism Responsible for closure of epiphyseal plate. Influences sexual behavior Supports final maturation of sperm Stimulates development of secondary mad sex characteristics Male problem’s and things that just happen. • Nocturnal emissions: involuntary ejaculation during sleep (wet dreams) • Enlarged prostate: inflammation of prostate, usually from an infection. • Prostate cancer: most frequently diagnosed cancer and 2nd leading cause of cancer death • Testicular cancer: 1-2% of all cancers that occurs in males. • Anabolic steroids: A group of steroids that promote storage of proteins and growth of tissues. • sterility: The inability to fertilize the ovum. • • • • • • • • Vagina Vulva Mons pubis labia majora Labia minora Clitoris prepuce Vestibule • • • • • Ovaries Uterus Fallopian tubes Cervix perineum The Vagina • Tubular, fibro muscular organ lined with mucus membranes. • Functions – The vagina is the passage way for spermatozoa and menstrual flow – The lower part of the birth canal – Receptacle for penis during intercourse Functional features of the vagina • The vagina has three functional features. – The fornix: the proximal area that surrounds the vaginal attachment of cervix. – The Rugae: Transverse folds in the vagina – The Hymen: a thin fold of vascular mucus membrane, forms boarder around vaginal orifice partially closing it. • Vulva: external genitalia • Mons Pubis: a mound of adipose tissue and pubic hair over the pubic bone. • Labia Majora: the outer lips of the vulva. • Labia Minora: The inner lips of the vulva, one on each side of the vaginal opening. • Vestibule: Area of the vulva inside the labia minora. • Clitoris: Small cylindrical mass of nerves and erectile tissue. • Prepuce or Clitoral hood: The foreskin or fold of skin over the clitoris. • Ovaries: female Gonads, almond shaped. Produce the female sex cells and hormones. • Fallopian tubes: Two tubes, extending from the sides of the uterus, in which the egg and sperm travel. • Perineum: The area between the vagina and anus. The uterus • Pear shaped organ inside the female pelvis, sectioned into three sections. – Fundus: superior dome, openings above the opening to the fallopian tubes. – Body: major tapering, central portion of uterus. – Cervix: narrow thick muscular area that opens into the vagina. Layers of the Uterus • Perimetrium: otter most layer of uterus which provides a small amount of protection to the uterus • Myometrium: middle, smooth muscle layer. The majority of uterus is made of myometrium. • Endometrium: inner layer, layer that is shed during menstruation. Menopause • Menstrual cycle becomes less frequent. • Ovaries fail to respond to FHS and LH hormones • Physical atrophy of ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina and external genitals • Increase of osteoporosis • Increase for cardiovascular diseases • Symptoms include: hot flashes, weight gain and depression. Female reproduction disorders • Ovarian Cysts: fluid filled sacs that form on the ovaries. • Yeast infections: A fungal infection that causes itching and a thick smell discharge. • Female infertility: The inability to become pregnant. • Endometriosis: The presence of tissue that normally grows inside the uterus in an abnormal anatomical location. If gone untreated it can cause infertility.