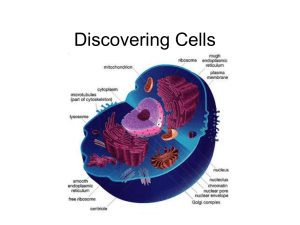
The Organization of Living Things
advertisement

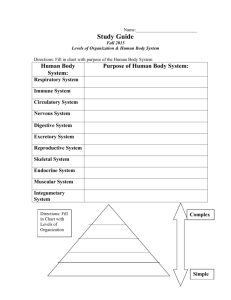
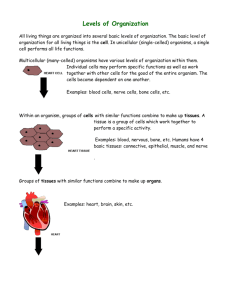
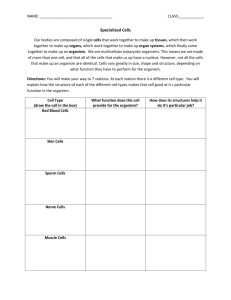
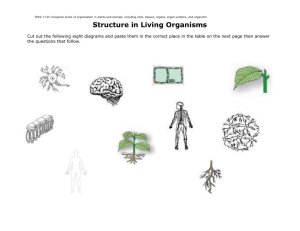
By Carla Bridges Why can’t you use your arm muscles to digest food? You Are!!!!!!!!!! An organism made of many cells. Made by making more small cells, not by making cells larger. For example: Elephant vs. human Larger 1. 2. 3. Size Larger than single celled organisms Prey for less predators Wider variety of prey Longer Life 1. Is not limited to the lifespan of a single cell Specialization 1. Each cell has a specific job. 2. Makes organism more efficient Tissue-group of cells that work together to perform a specific job. Material around and between the cells is also part of the tissue. Animals 1. 2. 3. 4. have four types of tissue Nerve tissue Muscle tissue Connective tissue Protective tissue Plants have three types of tissue: 1. Transport tissuemoves water and nutrients through a plant 2. Protective tissuecovers the plant; helps the plant retain water, protection 3. Ground tissuephotosynthesis takes place here Organ - a structure made up of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific function Has several kinds of tissue. Muscle tissue makes food move in and through the stomach. Special tissues make chemicals that help digest your food. Connective tissue holds the stomach together. Nervous tissue carries messages back and forth between the stomach and the brain. Larger Size Longer Life Cell Specialization Organ - a structure made up of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific function A group of organs working together to perform a particular function is called an organ system. Each organ system has a specific job to do in the body. Plants have organ systems also: Leaf system Stem system Root system Digestive system Stomach and Intestines 1. Job is to break down food into small particles. 2. The rest of the body depends on the digestive system for fuel. The digestive system depends on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems for oxygen. Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Carries fuel to the rest of the body Anything that can perform life processes by itself is an organism. 2 types Unicellular and multicellular Unicellular organisms Bacteria Protists Some Fungi Live in colonies but all of the cells are single cells Each cell must carry out all life processes to survive In Contrast: Even the simplest multicellular organism has specialized cells that depend on each other for the survival of the organism. Cell Tissue Organ Organ system Organism Structure is the arrangement of parts in an organism. Includes the shape of a part and the material of which the part is made. Example: The structure of the lungs is a large spongy sac. Function is the job the part does Example: The function of the lungs is to carry oxygen to the rest of the body. Connection; The structure of the lungs enables them to perform a function. Break into pairs according to shoe color Holt Science and Technology. Holt, Rinehart, and Winston. Harcourt Education Company. Austin, Texas 2005. UCP 1: Systems, order, and organization UCP 2: Evidence, models, and explanation UCP 5: Form and function LS 1a: Living systems at all levels of organization demonstrate the complementary nature of structure and function. Important levels of organization for structure and function include cells, organs, tissues, organ systems, whole organisms, and ecosystems. LS 1b: All organisms are composed of cells—the fundamental unit of life. Most organisms are single cells; other organisms, including humans, are multicellular. LS 1d: Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multicellular organisms. Groups of specialized cells cooperate to form a tissue, such as a muscle. Different tissues are in turn grouped together to form larger functional units, called organs. Each type of cell, tissue, or organ has a distinct structure and set of functions that serves the organism as a whole.