Cellular Organization: Levels & Types of Organisms
advertisement

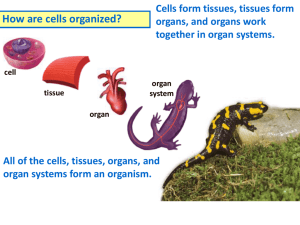
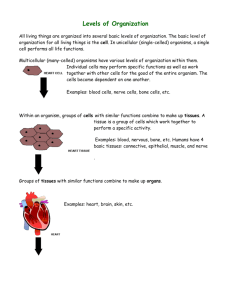
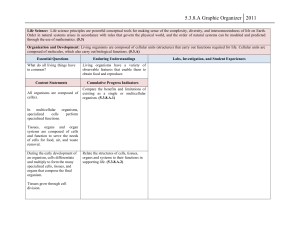
Cellular Organization Sec. 7-4 Interest Grabber Section 7- 4 From Simple to More Complex • Many multicellular organisms have structures called organs that have a specific function and work with other organs. Working together, these organs carry out the life processes of the entire organism. Go to Section: Interest Grabber continued 7- 4 • Section 1. Some activities cannot be performed by only one person, but need a team of people. What type of activity requires a team of people to work together in order to complete a task? • 2. What do you think are some characteristics of a successful team? • 3. How is a multicellular organism similar to a successful team? Go to Section: Section Outline Section 7- 4 • Go to Section: 7–4 The Diversity of Cellular Life – ALL cells use the same basic chemistry – Cells are specialized, as individuals or as parts of larger organisms – Grow, respond, reproduce A. Unicellular Organisms: Single celled organism - Dominate life on Earth - Prokaryotes - Bacteria – adaptable - Eukaryotes - Algae, Yeast (unicellular fungi), and Protists B. Multicellular Organisms: Made up of many cells that work together - Interdependent (team) - Cell specialization C. Levels of Organization 1. Cells: Basic living units of ALL organisms 2. Tissues: Group of similar cells that perform a particular function - 4 main types: muscle, epithelial (cover or line body), nervous, and connective (bone, blood, cartilage, and lymph) 3.Organs: Many groups of tissues working together 4.Organ Systems: Group of organs that work together to perform a specific function - 11 major organ systems: muscular, skeletal, circulatory, nervous, integumentary, respiratory, digestive, excretory, endocrine, reproductive, and immune Levels of Organization Section 7- 4 Muscle cell Go to Section: Smooth muscle tissue Stomach Digestive system