Organic Chemistry
advertisement

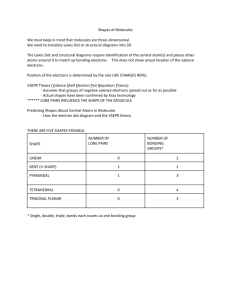
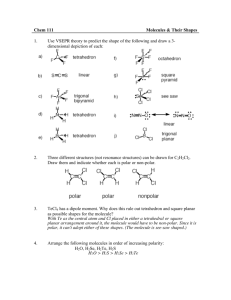
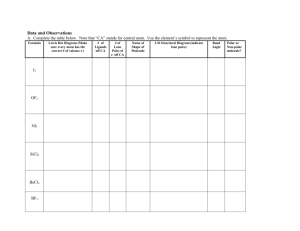
Organic Chemistry Nothing to do with organs Bonding in organic chemistry Covalent bonds – sharing electrons Nonpolar covalent bonds – electronegativity difference of less than 0.5 units Polar covalent – EN difference of 0.51.9 units EN difference of >1.9 is ionic (“DEN”) C–C DEN = 0, NPC Bonding in organic chemistry C–H DEN = 0.35, NPC H–Cl DEN = 0.94, PC d+ H Cl d– Lewis structures show all valence electrons – nonbonding as pairs of dots, and bonding as lines Bonding in organic chemistry methanol All atoms must have full octet H, halogens make one bond Bonding in organic chemistry (halogens have three lone pairs) O and S make two bonds (w/two lone pairs) N makes three bonds (one lone pair) C makes four bonds Double bonds – 4e-, represented by two lines Bonding in organic chemistry formic acid Triple bonds acrylonitrile Bonding in organic chemistry acetylene Shapes of molecules Bond angles – determined by valenceshell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) between ligands (bonded group or lone pair) Molecule Shapes Four groups – tetrahedral shape, 109.5º bond angles – ex. CH4 methane Molecule Shapes If one of the four groups is a lone pair, then the shape is trigonal pyramidal (ammonia) Molecule Shapes H-N-H angles are 107.3º In water (bent geometry) H-O-H angles are 104.5º Molecule Shapes Three groups – trigonal planar shape, 120º bond angles – BF3 Molecule Shapes If ligands are not identical, then angles will deviate from 120º Molecule Shapes Two groups – linear shape, 180º bond angles Molecule Shapes Molecular polarity – a molecule is polar if it has polar bonds and asymmetry Polar examples: water, ammonia, methanol Nonpolar examples (with polar bonds): CO2, CCl4 Nonpolar examples (no polar bonds): methane, benzene Functional groups Contain N, O, S, or halogens Are often the site of chemical reactivity of a molecule Used to divide organic compounds into classes Used as basis for naming organic compounds Functional groups Alcohols -OH (hydroxyl) primary (1º) alcohol (methanol) Functional groups secondary (2º) alcohol (2-propanol or isopropanol) CH3CHOHCH3 Functional groups Tertiary (3º) alcohol (2-methyl-2propanol or t-butyl alcohol) Draw all the alcohol isomers of C4H10O and label each as a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol. Functional groups Amines –NR2 (amino – R can be H or a carbon containing group) Ammonia – NH3 1º amine – CH3CH2NH2 2º amine – CH3NHCH3 3º amine – (CH3)3N Functional groups Aldehydes and ketones R2C=O (carbonyl) Ketone (acetone) Aldehyde (acetaldehyde) Functional groups Carboxylic acids RCOOH (carboxyl group) Acetic acid