Computer Networking Fundamentals: Topologies & Protocols
advertisement

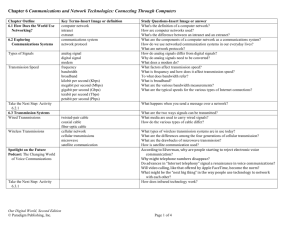
Computer Networking (Appendix C) Objectives • Understand networking fundamentals • Understand network services and transmission media • Understand network software and hardware Networking Fundamentals • Network consists of: – Servers – provides services – Clients – requests services – Peers – both requests and provides services • Types of networks – Server-centric networks – Peer-to-peer networks Networking Fundamentals • Network Services – – – – File services Print services Message services Applications services Networking Fundamentals • Network Operating System (NOS) – Two parts: • System software that runs on the server • Client software on each workstation – Examples • • • • Banyan Vines Novell NetWare Microsoft LAN Manager LANtastic Networking Fundamentals • Transmission Media – The pathway to send data and information between two or more entities on a network – Bandwidth: transmission capacity – Attenuation: weakening of a signal over distance – EMI: electromagnetic interference Networking Fundamentals • Cable Media – Twisted pair cable – Coaxial cable (“coax”) – Fiber-optic cable Networking Fundamentals • Wireless Media – Infrared line of sight – High-frequency radio • Pager – one way wireless • Cellular phone – two way wireless • Wireless LANs – Microwave • Terrestrial • Satellite Network Software and Hardware • Media access control – Rules that govern how a workstation gains access to the network • Distributed access control – Token passing • Random access control – “Listens” for network traffic Network Software and Hardware • Network topologies – Star network – Ring network – Bus network A star network topology • Use: This topology is useful for applications where processing must be centralized and some can be performed locally. • Advantages: – Easy to lay out and modify. – It is easy to diagnose problems at individual workstations. • Problems: – Costly, it requires the largest amount if cabling. – Since all communication pass through the central computer, the communications in the network will stop if the host/hub computer stops functioning. A ring network topology • Use: This topology is useful in LANs. • Advantages: – It does not rely on central host. – The connecting wire, cable, or optical fiber forms a closed loop. Data are passed along the ring from one computer to another and always flow in one direction. The message is regenerated and passed to the next computer if it is not for the previous computer. This regeneration process enables ring networks to cover much larger distances than star or bus networks. • Disadvantages: – A failure of any node on the ring network can cause complete network failure. – It is difficult to modify and reconfigure the network. A bus network topology • Use: This topology is useful in LANs. • Advantages: – It does not rely on central host. – This network can still function if one of the computers malfunctions. – Other advantages: easy to wire, quick response, less expensive. • Disadvantages: • The main disadvantage is bad connection to the cable can bring down the entire network. Another problem: collision occurs when 2 nodes send messages simultaneously. Network Software and Hardware • Protocols: Set of rules ( format of transmitting data, error checking method, data compression technique) – OSI model – open systems interconnection – Ethernet – TCP/IP OSI RM OSI RM Network Software and Hardware • Connectivity hardware 1. Transmission Media Connectors: T-connector for coax cable and RJ-45 connectors for twisted pair 2. Network interface card (NIC) 3. Modems 4. Repeaters 5. Hubs 6. Bridges 7. Multiplexers 8. Routers 9. Brouters 10. Channel service units (CSU): buffer between a LAN and a WAN 11. Gateway