Soil and Plant Nutrition
advertisement

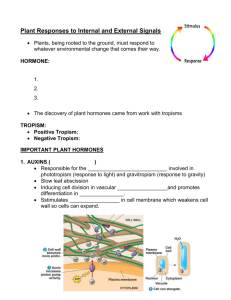
Response to Signals in Plants Chapter 39 Signal Transduction Pathway 1. Receptors receive a stimulus and activate the secondary messengers 2. Secondary messengers ______ the signal in other proteins 3. Cells respond to the signal 1. _____________ pathway 2. Transcriptional regulation Signal Transduction Pathway 1. Light signal activates __________ receptor which initiates two signal transduction pathways 2. Each transduction pathway activates kinase protein 3. Kinase proteins activate the expression of genes that result in a _______ (de-etiolation) response 2 1 3 Plant Hormones Hormone: _____________ produced in one part of an organisms body, which _______ another part of the body where it binds with a specific receptor and initiates a response in target cells or tissues Auxin (IAA) Cytokinins Gibberellins (GA) Abscisic acid (ABA) Ethylene Brassinosteroids Jasmonates Strigolactones Hormone: Auxin (IAA) Primary location produced: Shoot apical meristem Young leaves Major functions: Stimulates _____________ Promotes lateral and adventitious root formation Regulates ______________ Phototropism and gravitropism Promotes secondary growth Polar Transport of Auxin Auxin is transported from apex to shoot Cell wall is _____ Auxin ion picks up H+ Diffuses across plasma membrane Cytosol is _______ Auxin loses H+ Uses energy to pump out H+ to maintain pH Leaves cell through carrier proteins Cell Elongation in Response to Auxin 3 Low pH activates __________, which separate microfibrils and polysaccharides Hormone: Cytokinins Primary location produced in plant: Roots Major functions: Regulate _________ (cytokinesis) and influence pathway of differentiation More cytokinins = development of shoot buds More auxins = more root growth Control apical dominance = apical bud __________________ of axillary buds Promote lateral bud growth Stimulate seed germination Delays senescence (death or deterioration of plant parts) Apical Dominance Hormone: Gibberellins (GA) Primary location produced in plant: Apical meristems of roots and buds Young leaves Developing seeds Major functions: Stimulate ____________ and _________ Pollen development and tube growth Promotes _____________ and germination Stimulates flowering and fruits (with auxin) Gibberellins Role in Germination 1. After being activated by water, gibberellins are released, which signal the aleurone 2. Aleurone releases _____________, which breakdown endosperm 3. Nutrients provide energy to developing embryo Hormone: Abscisic acid (ABA) Primary location produced in plant: All plant cells Major functions: ______ growth Controls stomata under water stress Promotes seed dormancy (counteracts gibberellins) Promotes leaf senescence (programed death) Hormone: Ethylene Primary location produced in plant: Most plant cells Major functions: Triple response of seedlings 1. 2. 3. Slow stem elongation Thickening of stem Horizontal growth of stem Promotes ______ ___________ (detachment) Senescence Movement in Plants Tropism: a directional growth response toward or away from a stimuli _____________: directional growth in response to light Caused by concentration of Auxin on shaded side Movement in Plants Gravitropism: directional growth in response to _____ Caused by sedimentation of _______ in plant cells. Movement in Plants Thigmotropism: directional growth in response to _____ Plant Response to Light Blue-light photoreceptors Initiate phototropism Opening of ______ Slowing of seed leaf stem (hypocotyl) after seedling breaks ground Plant Response to Light Phytochromes (receptors that absorb mostly red-light) De-etiolation (greening) Seed germination Triggered by accumulation of red and far-red phytochromes Red phytochrome (Pr) Far-red phytochrome (Pfr) ______ growth ________ growth Shade avoidance Pr and Pfr ratio dictate growth Responses to Pfr: • Seed germination • Inhibition of vertical growth and stimulation of branching • Setting internal clocks • Control of flowering Daily and Seasonal Plant Responses Circadian rhythms: around 24-hr cycles that are not directly controlled by a known environmental variable Photoperiodism: a physiological response to photoperiod (interval an organism is exposed to light in a 24-hr period) Flowering (short-day vs. long-day) Critical night length Short-day and Long-day Plants Short-day plants: require light period ______ than some critical period Long-day plants: require light period _____ than some critical period Critical Night Length Some plants require a critical night length (ex. 12-hrs) to flower Flowering can be turned on or off by activating the red (Pr) and far-red (Pfr) phytocrome receptors Flowering Hormone Flower inducing hormone (______) can initiate flowering in plants not-triggered by photoperiod Plant Response to Environmental Stresses Drought stress Reduce transpiration Close _______ Release of __________ Inhibits growth of young leaves Change leaf shape Deeper root growth Drop leaves Dormant Encilia californica Plant Response to Environmental Stresses Oxygen deprivation Formation of aerial root _____ of root cortex cells to create air tubes Ethylene Plant Response to Environmental Stresses Salt Stress Salt glands Production of compatible solutes Maintain water potential Plant Response to Environmental Stresses Heat Stress ________ proteins Chaperone proteins Plant Response to Environmental Stresses Cold Stress Alter lipid concentration of membranes Changes in solute concentration of cytosol ________ proteins Plant Response to Pathogens PAMP triggered immunity Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) = ________________ specific to certain pathogens Effectors act to cripple host plants innate immune response R proteins Hypersensitive response = localized ____ _______ near infection site Lesions Systemic acquired response = signaling molecules activate defense system in entire plant Plant Response to Pathogens 1. Pathogen effector binds with R protein in host plant cell 2. R protein initiates a signal transduction pathway 3. __________________. Infected area is sealed off, with cell walls reinforced. Anti-microbial molecules are released and infected area dies. 4. Infected cells release signaling molecule 5. Signaling molecule transported throughout plant 6. Signaling molecule initiates signal transduction pathway 7. _____________________. Plant cells produce molecules that protect the cell from pathogens. Plant Response to Herbivores Herbivory: animals eating plants Recruitment of _____________ Plant Response to Herbivores Production of _______________ Tannins Opium Plant Response to Herbivores Timing of flowering