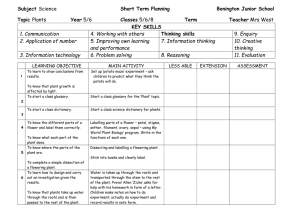
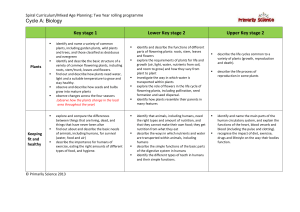
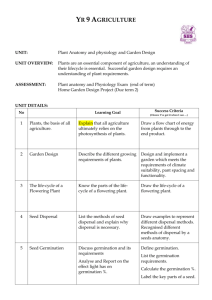
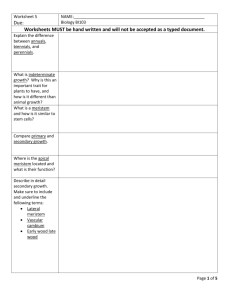
The Genetic Basis of Growth and Development
advertisement

The Genetic Basis of Growth and Development Plants are made up of • cells • tissues • organs Plants have specialized tissues called meristems • Shoot apical meristem (SAM) • Intercalary meristem • Root apical meristem (RAM) • Lateral meristems: pericycle, vascular cambium Plants grow by cell • division • expansion • differentiation Plant development is controlled by hormones • Auxin:stimulates growth and cell division • Gibberellins:stimulates stem growth and seed germination • Cytokinins:regulates cell division and senescence • Abscisic Acid:responds to osmotic stress, inhibits germination, closes guard cells More Hormones • Ethylene:regulates fruit ripening and flowering, responds to stress • Jasmonic Acid:responds to insect attacks turning on plant defenses • Brassinosteroids: affect stem elongation, pollen tube growth, leaf bending and xylem differentiation Plant development is affected by the environment • • • • • Phototropism (light) Gravitropism (gravity) Thigmotropism (touch) Nyctinastic movement (light) Thigmonastic movement (mechanical) Environmental Influences • Circadian Rhythms (biological clocks set by light) • Dormancy (temperature, light & water) • Vernalization (cold induction of flowering) • Stratification (cold induction of germination) • Photoperiodism (germination and flowering) Photoperiodic regulation of flowering Genetic control of flowering Signal transduction by hormones or environmental signals Genetic modification can redirect developmental processes • • • • • Male sterility for hybrid seed production Fruit ripening Senescence Delaying seed pod splitting Flowering