Auxin
advertisement

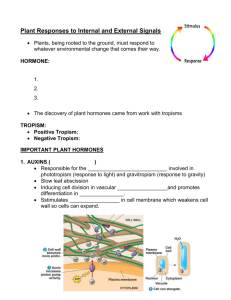
Growth Responses and Regulation of Growth CHAPTER 11 GROWTH & DEVELOPMENT Growth- the increase in size of a plant Development- the gradual changes over the life of the plant Both are controlled by Genetics Hormones (ex. Auxins, gibberellin…) Environment (ex. Tropism) WHAT ARE HORMONES? Organic compounds that act as chemical signals between cells Regulate growth & development 5 MAJOR CLASSES OF PLANT HORMONES 5. Auxin Gibberellin Cytokinin Ethylene Abscisic Acid Basically, these are just signaling molecules 1. 2. 3. 4. AUXIN Hormone involved in Stem elongation Apical dominance (inhibition of lateral growth) Encourages Helps root formation on cuttings plant grow towards light Targets cells that are not reached by light (in shade) Responsible for Phototropism Animation AUXIN AND PHOTOTROPISM Coleoptile = the first leaf of a monocot seedling AUXIN AND ROOT DEVELOPMENT Control (roots placed in water) LOW AUXIN CONCENTRATION HIGH AUXIN CONCENTRATION GIBBERELLIN Hormone involved in Stem elongation Flowering Seed germination EFFECTS OF GIBBERELIN CYTOKININ Hormone involved in REQUIRED Delay FOR CELL DIVISION!!! of senescence (aging) Interacts with auxin in the control of apical dominance (encouraging primary growth) HORMONES AND TISSUE CULTURE CYTOKININ AND SENESCENCE ETHYLENE A gaseous plant hormone involved in Leaf abscissions (the normal falling off of leaves/fruits/flowers) Ripens fruits Weakening Leaf cell walls during autumn senescence (aging) ETHYLENE AND FRUIT RIPENING ABSCISIC ACID Plant Hormone involved in Dormancy (temporary state of arrest/growth does not occur) Response Ex. to stress Drought – triggers closing of stomata PHOTOPERIODISM The response of a plant to the relative lengths of daylight and darkness (such as flowering) Short-day plants (long night) Flower when the night length is = or > ~ 12 hours Late Summer or fall Intermediate-day plants Do not flower when day is either too long or too short Spring or Fall Long-day plants (short night) Flower when night length is = or < 12 hours Late spring or summer Day-neutral plants photoperiod does not affect flowering TEMPERATURE AND REPRODUCTION Vernalization The low-temp requirement for flowering in some plant species Some plants need to be exposed to low temp for several weeks for flowering to occur after seeds germinate and grow Example of plant with low T requirement: Winter Wheat: planted in fall and germinates. Seedlings exposed to cold winter Flower after resuming growth in spring TEMPERATURE REQUIREMENTS TROPISM A tropism is a directional growth response Permanent change in position 3 types of tropism Phototropism - Stimulus photo = “light” Gravitropism – Stimulus grav = “weight” Thigmotropism – Stimulus thigmo = “touch” TROPISMS PHOTOTROPISM Directional GRAVITROPISM Plant growth of a plant caused by light growth in response to direction of gravity THIGMOTROPISM Growth in response to contact with a solid object