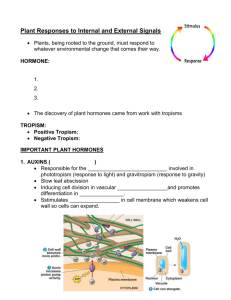
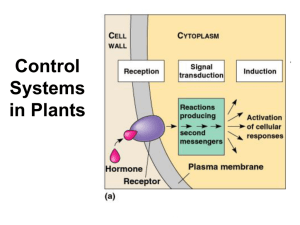
“Hormone” was first used to describe substances in
animals:
“a substance produced in a gland that circulates in
the blood and has an effect far away from the site
of production”
In plants used to mean a compound that acts at low
concentrations to affect growth and development.
Produced in one part of the plant and utilized in
another part.
Five plant hormones known by the mid 1960s,
new compounds called plant growth regulators.
•The five classical
hormones
–Auxins
–Cytokinins
–Gibberellins
–Ethylene
–Abscisic acid
•Other plant growth
regulators
–Brassinosteroids
–Salicylic acid
–Jasmonic acid
–Systemin
–Florigen
Hormones
Class
Endogenous Hormone
Growth Regulators
auxin
indoleacetic acid
IBA, NAA, 2,4-D, others
cytokinin
zeatin, zeatin riboside
kinetin, BA, 2iP, TDZ
gibberellin
GAx...125
GA3, GA4+7
abscisic acid
abscisic acid (ABA)
ethylene
ethylene
Ethephon, Ethrel
Frits Went’s experiments
Auxin (indoleacetic acid)
Produced in apical and root meristems, young leaves,
seeds in developing fruits
• cell elongation and expansion
• suppression of lateral bud growth
• initiation of adventitious roots
• stimulation of abscission (young fruits) or delay of
abscission
• hormone implicated in tropisms (photo-, gravi-,
thigmo-)
Auxin
•
•
•
•
Indole acetic acid and related molecules
Photo-and gravitropism
The shoot hormone, made in the shoot apex
Travels down the stem
– Polar Auxin Transport
Auxin promotes rooting
Auxin also:
• Promotes apical dominance
• Prevents leaf abscission
• Enhances fruit growth
– Auxin from the developing seeds results in fruit
growth
Auxin-like growth regulators
• indolebutyric acid (IBA)
• 2, 4 dichlorphenoxyacetic acid (2,4D)
• 2, 4, 5 trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4,
5 T)
• picloram
Napalm, Agent Orange, dioxin
Herbicide
•
•
•
•
2,4-D – 2,4 dichlorophenoxy acetic acid
Causes a plant to grow itself to death
More readily absorbed by broad-leaved plants
Most often the “weed” of ‘Weed and Feed’
lawn fertilizers
Commercial uses - auxins
• stimulation of adventitious rooting
• 2,4-D as a herbicide for dicots
• sprout prevention in pruned trees
• fruit thinning or fruit holding depending on stage
of development
Cytokinin
• Cytokinin – the root hormone
• Discovered by Folke Skoog
• The last unknown compound needed to get
plant cells to grow undifferentiated
• Cytokinins delay and even reverse senescence
• Release buds from apical dominance
Cytokinin (zeatin, ZR, IPA)
• cell division factor
• stimulates adventitious bud
formation
• delays senescence
• promotes some stages of root
development
Cytokinins
Cell division and cytokinesis
• - Moves in xylem sap
• - Stimulates RNA and protein synthesis
• - Works in conjunction with auxin
Apical dominance
• - Cytokinin and auxin are antagonistic- auxin from
terminal bud causes shoot to lengthen
• - Cytokinins from roots stimulate axillary bud
• -Auxin stimulates lateral root formation
cytokinins restrain it
• - Anti-aging - slows leaf deterioration
b.
Commercial uses - cytokinins
Applied as kinetin, benzyladenine, or zeatin conjugates
• axillary bud growth in orchids, daylilies
• antioxidant (browning preventer) in cut salads
• mix with GAs as fruit size stimulator
Gibberellins
• A large family of compounds (80) with a few
biologically active members
• Produced in roots and young leaves
• Now known to be essential for stem
elongation
• Dwarf plant varieties often lack gibberellins
Gibberellins
• Found as the toxin produced by some fungi
that caused rice to grow too tall – “Foolish
Disease”
• Induces parthenocarpic fruit development
• Delays senescence
• Gibberellins are involved in bolting of rosette
plants
• Gibberellins are used to improve grapes
• Gibberellins are involved in seed germination
– gibberellins will induce genes to make enzymes
that break down starch
Commercial uses - GA inhibitors
Cycocel, Bonsai, Sumagic
• height control in flowering pot plants (lilies,
orchids)
• height control in bedding plants
Commercial uses - GA application
Apply as GA3, or GA4+7
• increase flower size on certain ornamentals (eg,
“gibbing” camellias)
• increase berry separation and size in bunch grapes
• overcome shallow dormancies in vegetative buds
• stimulate seed germination
Ethylene
• The smallest hormone
• A gas
• Important in seed germination, fruit ripening,
epinasty, abscision of leaves
• Sex expression in cucurbits
Ethylene
Gaseous hormone produced in many plant tissues
• autocatalytic (stimulates its own production)
• volatile gas
• production stimulated during ripening, flooding,
stress, senescence, mechanical damage,
infection
• product of combustion of petrochemicals
Commercial uses - ethylene application
Applied as ethylene gas or Ethephon or Ethrel sprays
• flower initiation (bromelliads, pineapples)
• stimulation of ripening (bananas, tomatoes)
• degreening of citrus
• abscission induction prior to mechanical harvest
(cherries)
• increased color development in once-over harvested
processor type tomatoes
Commercial uses - ethylene inhibition
Removed by chemical “scrubbing” or low atmosphere
• long term storage of apples in CA storages
• treatment of cut flowers with silver thiosulfate
• long-keeper (delayed ripening) mutants (or rDNA) of
tomato
• hypobaric storage of many fruits, vegetables, flowers
Abscisic acid (ABA)
Found in stressed leaves, dormant seeds, dormant buds
• stomatal closure
• inhibits germination of some seeds
• inhibits active growth of axillary buds
Abscisic acid
•
•
•
•
•
Incorrectly named, not related to abscission
Important in water stress and other stresses
Causes stomatal closure
Prevents premature germination of seeds
Changes gene expression patterns