File
advertisement

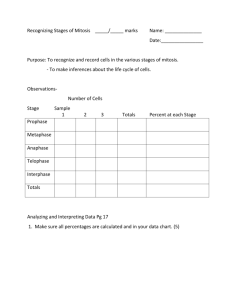
MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK G1 Interphase • In this example, we will examine a cell chromosomes (red, blue and containing 3_____________ green) in the initial parent cell. G2 Interphase • After S Phase, each chromosome has undergone DNA replication. There are now 3 duplicated chromosomes _______________________. • At this point, the DNA has _____________ not condensed yet so it is still ____ long and ____. thin This long _________ thread-like form of DNA is called _________. chromatin MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK G2 Interphase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK G2 Interphase • The two identical sides of each duplicated chromosome are called _______________. sister chromatids • The two sister chromatids are _________ connected together at a region of the chromosome called the centromere __________. • The centromere is where • microtubules protein structures called ___________ kinetochores assemble on either side of the sister chromatids. The kinetochores are the attachment for sites of __________ ___________ which pull ___ the kinetochores microtubules sister chromatids apart. sister chromatids centromere MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK G2 Interphase • The two identical sides of each duplicated chromosome are called _______________. sister chromatids • The two sister chromatids are _________ connected together at a region of the chromosome called the centromere __________. spindle fibers / microtubules • Microtubules ___________ are protein filaments that serve various different functions within a cell. When they are used in mitosis or meiosis, they can be specifically referred to spindle fibers as ____________. kinetochores sister chromatids centromere Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK PROPHASE nuclear membrane • The centrosomes begin to _______ migrate to opposite poles _____________. Spindle fibers begin • ____________ to form between the two centrosomes. membrane begins to dissolve • The nuclear ________________ _______ Why do you think the nuclear membrane needs to dissolve completely? QUICK TASK #5 Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK PROPHASE nuclear membrane • The centrosomes begin to _______ migrate to opposite poles _____________. Spindle fibers begin • ____________ to form between the two centrosomes. nucleolus membrane begins to dissolve • The nuclear ________________ _______ frees the chromosomes to be sorted which _____ and divided in later stages of mitosis. condense and • The chromatin begins to ________ visible become shorter ______ , thicker ______ and ______. • The nucleolus ________ begins to disappear. Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK METAPHASE Compare metaphase to prometaphase. What changes have occurred? QUICK TASK #7 Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK METAPHASE • The centrosomes are ____ fully migrated to opposite poles. • The spindle apparatus is completely _________ formed. fully dissolved. • The nuclear membrane is ____ lined up the • The spindle fibers have _______ duplicated chromosomes along the equatorial plate so that each sister _____________ chromatid of a duplicated chromosome faces opposite _______ poles. Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK METAPHASE • The centrosomes are ____ fully migrated to opposite poles. • The spindle apparatus is completely _________ formed. alignment at this stage helps to • Correct _________ ensure that each new daughter cell will receive one sister chromatid from each duplicated chromosome when the sister chromatids are separated. Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK METAPHASE • At this stage, the chromosomes are thick ____, _____ short and at their most condensed _________, hence the chromosomes are at their most easily observable state. sister chromatid centromere Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK ANAPHASE Compare anaphase to metaphase. What changes have occurred? QUICK TASK #8 Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK ANAPHASE • Each chromatid becomes its own ___________ chromosome once separation has occurred. shorten • The kinetochore __________ spindle fibers _______ and ____ pull the attached sister chromatids apart at the __________ centromere towards opposite poles. • The polar ____ spindle fibers push against each other to elongate _______ the cell and further separate the sister chromatids. Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK TELOPHASE Compare telophase to anaphase. What changes have occurred? QUICK TASK #9 Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK TELOPHASE • This phase is essentially the reverse ______ of prophase. • The spindle apparatus begins to disassemble __________. • The chromosomes become ____ long and thin decondensing and reverting ___ by ____________ chromatin structure. back to their _________ membrane begins to reform • A nuclear ________________ around each set of chromosomes. • The nucleolus ________ reappears in each nucleus. Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK TELOPHASE cleavage furrow furrow (or ________ cell plate in • A cleavage _____________ plant cells) begins to form which signals the beginning of __________ cytokinesis which will separate the two new daughter cells. Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK prophase A anaphase B telophase C interphase D metaphase E How many did you get correct? ACTIVITY #2 Identify cells A-E as interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase or telophase. (There’s no prometaphase example in this image.) Telophase MITOSIS ProAnaphase Metaphase metaphase Prophase MITOSIS – A DETAILED LOOK Mitosis (Overview) PLAY The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (Detailed) PLAY