Blood and Bone Marrow
advertisement

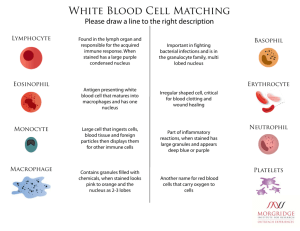
Blood and Bone Marrow Histology SSN November 18, 2004 Presented by: Nadia Goodwin & Missy Walker Formed Elements of the Blood Peripheral Blood: Erythrocytes • RBCs constitute the largest number of cells in the blood • Biconcave discs • NO NUCLEUS • Contain Hemoglobin Peripheral Blood: Platelets • Derived from Megakaryocytes in bone marrow – formed from small bits of Megakaryocyte cytoplasm • Function in blood clotting Peripheral Blood: Leukocytes • GRANULOCYTES – Neutrophils – Basophils – Eosinophils • AGRANULOCYTES – Lymphocytes (T and B cells) – Monocytes (Macrophages) Peripheral Blood: Leukocytes • GRANULOCYTES – Neutrophils – Basophils – Eosinophils Granulocytes: Neutrophils • Most numerous WBC in blood • Multilobed nucleus • Granules: – Azurophilic granules – Specific granules • Function – 1st wave of cells in acute inflammation; can phagocytose bacteria Granulocytes: Basophils • Rare! • Lobulated nucleus often obscured by granules • Dark Blue Granules – Hydrolytic enzymes, heparin sulfate, histamine, SRS • Function – Role in hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis Granulocytes: Eosinophils • Bilobed nucleus • Bright pink Granules – Arginine rich major basic protein, peroxidase, histaminase, arylsulfatase • Function: – Important in allergic rxns, parasitic infections, and phagocytosis of Ab-Ag complexes Agranulocytes: Monocytes • Largest WBCs in blood smear • Migrate through blood to the tissues; once in tissues they differentiate into phagocytes (macrophages) Agranulocytes: Lymphocytes • About size of RBCs • Function – Main functional cells of adaptive immune system – T cells – B cells Questions Which of the following cell types would be expected to be increased in number with a bacterial infection? Viral? Parasitic? RBC Development Watch for trends! Proerythroblast • Biggest in lineage • Large central nucleus with one or two nucleoli • Basophilic cytoplasm b/c ribosomes • Look for Golgi ghost Basophilic Erythroblast • Smaller than proerythroblast • Checkerboard nucleus (heterochromatic) • Intense basophilia (lots of ribosomes!) Proerythroblast vs Basophilic Erythroblast Polychromatophilic Erythroblast • Smaller than basophilic erythroblast • Smaller intensely heterochromatic nucleus • Purple/lilac cytoplasm mix of basophilia from ribosomes and growing eosinophilia from hemoglobin • LAST MITOTIC STAGE! Normoblast • Smaller than polychromatophilic erythroblast • Small, compact, intensely staining nucleus that is getting ready to be extruded • Eosinophilic cytoplasm due to abundant hemoglobin Reticulocyte • Immature RBC that has polyribosomes • Appear as polychromatophilic erythrocyte on blood smear • When stained with a special (supravital) stain Reticulocyte Erythrocyte • Smallest • Eosinophilic due to hemoglobin • NO NUCLEUS! Erythropoiesis Development of Granulocytes What are the Granulocytes? These are cells of the immune system (White Blood Cells) that contain vesicles. The vesicle contents vary among cell lines and stain differently. • Neutrophils (polymorphonuclear or PMN cells) • Eosinophils • Basophils Trend of Development • Larger to smaller • Azure granules to specific granules • Round nucleus to altered shape nucleus Granulocyte Lineage: Myeloblast → Promyelocyte → Myelocyte → Metamyelocyte → Band → Granulocyte (Erythroid: Proerythroblast →Basophilic erythroblast → Polychromatophilic erythroblast → Normoblast → Reticulocyte → Erythrocyte) Myeloblast Prominent nucleoli PROmyelocyte • Details • Golgi ghost • Can’t distinguish type of granulocyte yet • Eccentric nucleus • Don’t confuse with proerythroblast or basophilic erythroblasts Myelocyte • Last stage in which mitosis can occur • Begin to see who’s a neutrophil, who’s an eosinophil (who’s a basophil) • Golgi ghost Neutrophilic Myelocyte vs Eosinophilic Myelocyte METAmyelocyte • nucleus changing shape, not spherical • Soooo . . . No more mitosis Band Cell • Immature granulocyte • Elongated nucleus of nearly uniform width; horseshoe/U-shaped Finally . . . Myeloblast – no granules capable of mitosis Promyelocyte – azurophilic granules Mylocyte – specific granules Metamylocyte – specifc granules nucleus changes shape Band cell – (PMN only) specific granules Mature Granulocyte – specific granules Compare what you see . . . Megakaryocyte • Huge • Platelets form from invaginations of this • Multilobular nucleus Megakaryocyte Don’t Worry, Be Happy!