Blood and Bone Marrow
advertisement

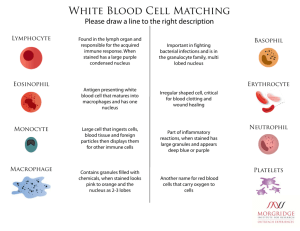
Eosinophil Peripheral Blood Erythrocytes = RBCs • NO NUCLEUS • Contain hemoglobin Platelets Leukocytes = WBCs • Granulocytes • Neutrophils = PMNs = “polys” • Eosinophils = “eos” • Basophils = “basos” • Agranulocytes • Lymphocytes = T and B cells • B cells plasma cells • Monocytes Macrophages (MΦ) Granulocytes PMN Eos PMN Baso Neutrophils • Numerous • Multilobed nucleus • Azurophilic & Specific granules • Phagocytose bacteria Basophils • Rare! • Lobulated nucleus often obscured by granules • Dark Blue Granules • Hydrolytic enzymes, heparin sulfate, histamine, SRS • Function • Role in hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis Eosinophils • Bilobed nucleus • Bright pink Granules • Arginine rich major basic protein, peroxidase, histaminase, arylsulfatase • Function: • Important in allergic rxns, parasitic infections, and phagocytosis of Ab-Ag complexes Monocytes • Largest WBCs in blood smear • Migrate through blood to the tissues; once in tissues they differentiate into phagocytes (macrophages, osteoclasts) Lymphocytes • About size of RBCs • Function • Adaptive immune system • T & B cells Questions Which of the below cell types would increase in number with a bacterial infection? Viral? Parasitic? Bone Marrow Smear Erythropoesis Proerythroblast • Biggest in lineage • Large central nucleus with one or two nucleoli • Basophilic cytoplasm b/c ribosomes • Look for Golgi ghost Basophilic Erythroblast • Smaller than proerythroblast • Checkerboard nucleus (heterochromatic) • Intense basophilia (lots of ribosomes!) Proerythroblast vs Basophilic Erythroblast Polychromatophilic Erythroblast • Smaller than basophilic erythroblast • Smaller intensely heterochromatic nucleus • Purple/lilac cytoplasm mix of basophilia from ribosomes and growing eosinophilia from hemoglobin • LAST MITOTIC STAGE! Normoblast • Smaller than polychromatophilic erythroblast • Small, compact, intensely staining nucleus that is getting ready to be extruded • Eosinophilic cytoplasm due to abundant hemoglobin Reticulocyte • Immature RBC that has polyribosomes • Appear as polychromatophilic erythrocyte on blood smear • When stained with a special (supravital) stain Reticulocyte Erythrocyte • Smallest • Eosinophilic due to hemoglobin • NO NUCLEUS! Review Granulopoesis Ross Fig 9-18 p. 235 Development of Granulocyte (focus on PMN) What are Granulocytes? • WBCs that contain specific granules • Granule contents vary between cell types and stain differently • Neutrophils (“polys” or PMNs) • Eosinophils • Basophils Trend of Development • • • Larger smaller Azure granules specific granules Round nucleus altered shape nucleus Granulocyte Lineage: Myeloblast → Promyelocyte → Myelocyte → Metamyelocyte → Band → Granulocyte Myeloblast Prominent nucleoli PROmyelocyte • Details • Golgi ghost • Can’t distinguish type of granulocyte yet • Eccentric nucleus • Don’t confuse with proerythroblast or basophilic erythroblasts Myelocyte • Last stage in which mitosis can occur • Begin to see who’s a neutrophil, who’s an eosinophil (who’s a basophil) • Golgi ghost Neutrophilic Myelocyte vs Eosinophilic Myelocyte METAmyelocyte • nucleus changing shape, not spherical • No more mitosis Band Cell • Immature granulocyte • Elongated nucleus of nearly uniform width; horseshoe/U-shaped Finally . . . Myeloblast – no granules capable of mitosis Promyelocyte – azurophilic granules Mylocyte – specific granules Metamylocyte – specific granules nucleus changes shape Band cell – (PMN only) specific granules Mature Granulocyte – specific granules Review Compare what you see . . . Megakaryocyte • Huge • Platelets form from invaginations of this • Multilobular nucleus Monocyte Don’t Worry, Be Happy! Animations: http://www.medtraining.org/ltac/ User: library Password: cumed Click on the “Peripheral Blood” lesson