LEUKOCYTES
advertisement

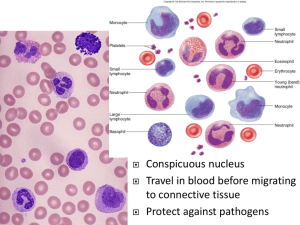
LEUKOCYTES (White Blood Cells) Classes • 2 main classes: • Granulocytes – have a grainy cytoplasm • Agranulocytes – have a clear cytoplasm Types There are 5 types of white blood cells: Granulocytes • Neutrophils 40-75% • Eosinophils 5% • Basophils 0.5% Agranulocytes • Lymphocytes 20-50% • Monocytes 1-5% The range is because the requirement for different types of WBCs vary from time to time. Neutrophils Structure: • Multilobed nucleus • Inconspicuous granules Amount: • 3-7,000/mm³ Functions: • Engulfing bacteria & viruses (phagocytosis) Life Span: • hours → days Eosinophils Structure: • Bilobed nucleus • Large, red granules Amount: • 100-400/mm³ Functions: • phagocytosis • Protects against parasitic infections • Neutralize histamines (their amts. incr. during hay fever & allergy attacks) Life Span – hours → days Basophils Structure: • Lobed nucleus • Large granules, but fewer Amount: • 20-50/mm³ Functions: • Become mast cells when they leave b.v. & produce histamines • Respond to allergens rapidly (anaphylactic shock) • Produce heparin (anticoagulant) Life Span – hours → days Monocytes Structure: • Largest WBC • U-shaped nucleus • Grayish blue cytoplasm Amount: • 100-700/mm³ Functions: • Phagocytosis • Become macrophages & remove dead cells Life Span – weeks → months Lymphocytes Structure: • Most numerous in children; 2nd most in adults • Spherical nucleus • Small “ring”of cytoplasm; pale blue Amount: • 1500-3000/mm³ Functions: • T cells – attack foreign antigens directly • B cells – produce antibodies for immunity Life Span – months → lifetime White Blood Cell Count • Normal adult has 5,000-10,000 cells/mm3 • Leukocytosis- WBC count above 10,000 cells/mm3 – Can be a sign of acute infection – Occurs during times of stress and vigorous exercise. • Leukopenia- WBC below above 10,000 cells/mm3 – Can be a sign of virus such as influenza, measles, mumps and HIV