Forces PowerPoint #2
advertisement

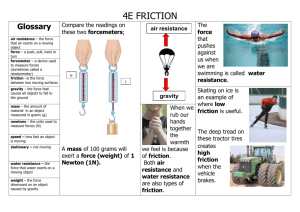
Forces *You can measure force using the spring scale at a grocery store. *A force is measured in newtons. *one newton is equal to one kilogram meter per second squared This picture is an example of the definition of force. Force Newton Push or pull that acts on an object The measurement of force *You can us an arrow to represent the direction and strength of a force. *Sometimes the net force acting upon an object is zero when the forces are equal. This Picture is an example of unbalanced forces. Net Force Overall force acting on an object after all forces are combined Friction A force that opposes the motion of objects that that touch as they move past each other *Examples of balanced forces are very common *Often the forces on an object are unbalanced. The man is doing work by pushing the block and the result Is the block moving Static Friction The friction force that acts on objects that are not moving Sliding Friction A force that opposes the direction or the motion of an object *Gravity is an attractive force that is a natural part of the earth . *Momentum doesn’t increase or decrease. This is the formula to find the amount of force acting upon an object. Rolling Friction The friction force that acts on an rolling object Fluid Friction Opposes the motion of an object through a fluid *Gravity is the weakest universal force. *Gravity is the most efficient force at a long distance. The lawnmower is experiencing rolling friction because its wheels are rolling on the ground. Air Resistance Fluid friction acting on an object in air Terminal Velocity Constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance equals the force of gravity. *Conservation means that something has a constant value. *Only when equal and opposite forces act on the same object do they result in a net force of zero This is an example of gravity because the apple is falling towards the center of the earth From the tree. Projectile Motion The motion of a falling object after it is given an initial forward velocity Gravity Force that acts on any of wo masses *Different types of friction act on moving and non-moving objects. *Sliding Friction acts to oppose the direction of motion. The stone launched forward because the driver stepped on the brakes too hard and caused inertia to come into play. The cat will fall when the car stops because there is not enough force to keep it sitting in the dashboard. Inertia Weight The tendency of an object to resist The force of gravity acting on an a change in its motion object *When an object rolls across the floor both the object and the floor are very slightly bent out of shape. *Friction acts on submarines moving through water and airplanes moving through air. This is another example of an unbalanced force because the other object tied to the rope has more force then the man. Mass Measure of inertia an object and depends on the amount of matter in the object Momentum Product of an objects mass and velocity *The force of gravity does not require contact with objects to be able to act on them. *Air resistance and gravity are the only forces acting on a projectile. This picture shows the car accelerating because the wheels are moving faster and faster over time. Law of Conservation of Momentum If no net force acts on a system then the total momentum of the system does not change Acceleration The rate at which velocity changes *As objects fall to the ground they accelerate and gain speed. *An unbalanced force is a result of forces that are acting on an object not being equal to each other. The balls mass and weight forms its momentum, which carries through the other balls to make the ball on the opposite end move. This cheetah is moving Very fast and has a high Velocity. Velocity Speed and direction an object is moving Instantaneous Speed Rate at which an object is moving at any given time *You can replace sliding friction with rolling friction. *Weight does not have an effect in how fast an object falls if both of the objects are the same type of object. The initial forward velocity of the object Slows as it falls to the ground. Constant Acceleration A steady change in velocity Birds and airplanes face fluid friction in the air the same way submarined face fluid friction in the water. Strong Nuclear Force Powerful force of attraction that acts only on the neutrons and protons in the nucleus *When you push on something you are using force. *Air resistance is the result of fluid friction in the air. The object has it’s force located In it’s center, making it a centripetal Force. Centripetal Force Center directed force that continuously changes the direction of an object to make it move in a circle Gravitational Force Is an attractive force that acts between any two masses